Imagine a future where your diet is tailored specifically to your genetic makeup, ensuring optimal health and well-being. This is the promise of personalized nutrition through nutrigenomics. In this article, we will explore the exciting world of nutrigenomics and how understanding our unique genetic variants can revolutionize the way we approach nutrition. From surprising statistics on genetic variants related to nutrition to practical tips for implementing personalized diet advice, we will delve into the benefits of a personalized nutrition approach and provide clear steps for readers to take action. Join us as we uncover the fascinating field of nutrigenomics and discover how it can pave the way to a healthier future.
Understanding Nutrigenomics
Defining Nutrigenomics
Nutrigenomics is the study of how individual genetic variations interact with specific nutrients in food and how these interactions can affect an individual’s health and risk of developing diseases. It combines the fields of genetics and nutrition to provide personalized dietary recommendations based on an individual’s unique genetic makeup.
Origins and History of Nutrigenomics
The field of nutrigenomics emerged in the late 20th century as researchers began to uncover the intricate relationship between genetics and nutrition. The Human Genome Project, completed in 2003, played a significant role in advancing our understanding of human genetics and paved the way for nutrigenomics research. Since then, scientists have been studying how specific genetic variations affect an individual’s response to different nutrients and how this knowledge can be used to optimize health and prevent disease.
Role of Nutrigenomics in Health
Nutrigenomics has the potential to revolutionize healthcare by providing personalized dietary recommendations that are tailored to an individual’s genetic makeup. By understanding how specific genetic variations impact nutrient metabolism, absorption, and utilization, healthcare professionals can develop targeted intervention strategies to promote optimal health and prevent and manage chronic diseases. Nutrigenomics can also help identify individuals who may be more prone to certain nutritional deficiencies or intolerances, allowing for early intervention and prevention of related health issues.
The Intersection of Genetics and Nutrition
Overview of Human Genetics
Human genetics is the study of the genes and genetic variations that make each individual unique. Genes are responsible for various traits and characteristics, including how our bodies metabolize and utilize nutrients. Understanding human genetics is crucial in nutrigenomics as it helps identify specific genetic variations that may influence an individual’s response to different nutrients and dietary patterns.
Effects of Nutrition on Gene Expression
Nutrition plays a vital role in gene expression, which refers to the process by which genes are “turned on” or “turned off.” Different nutrients and dietary components can influence gene expression, leading to changes in metabolic pathways, inflammation levels, and overall health. For example, certain nutrients, such as folate, have been found to influence DNA methylation, a process that can modify gene expression patterns and potentially impact disease risk.
Role of Genetics in Nutrition Absorption and Metabolism
Genetics can significantly impact an individual’s ability to absorb, metabolize, and utilize nutrients. Specific genetic variations can affect enzymes involved in nutrient metabolism, transporters responsible for nutrient absorption, and receptors that interact with nutrients in our bodies. By understanding these genetic variations, healthcare professionals can provide personalized dietary recommendations that take into account an individual’s unique genetic profile to optimize nutrient absorption and metabolism.
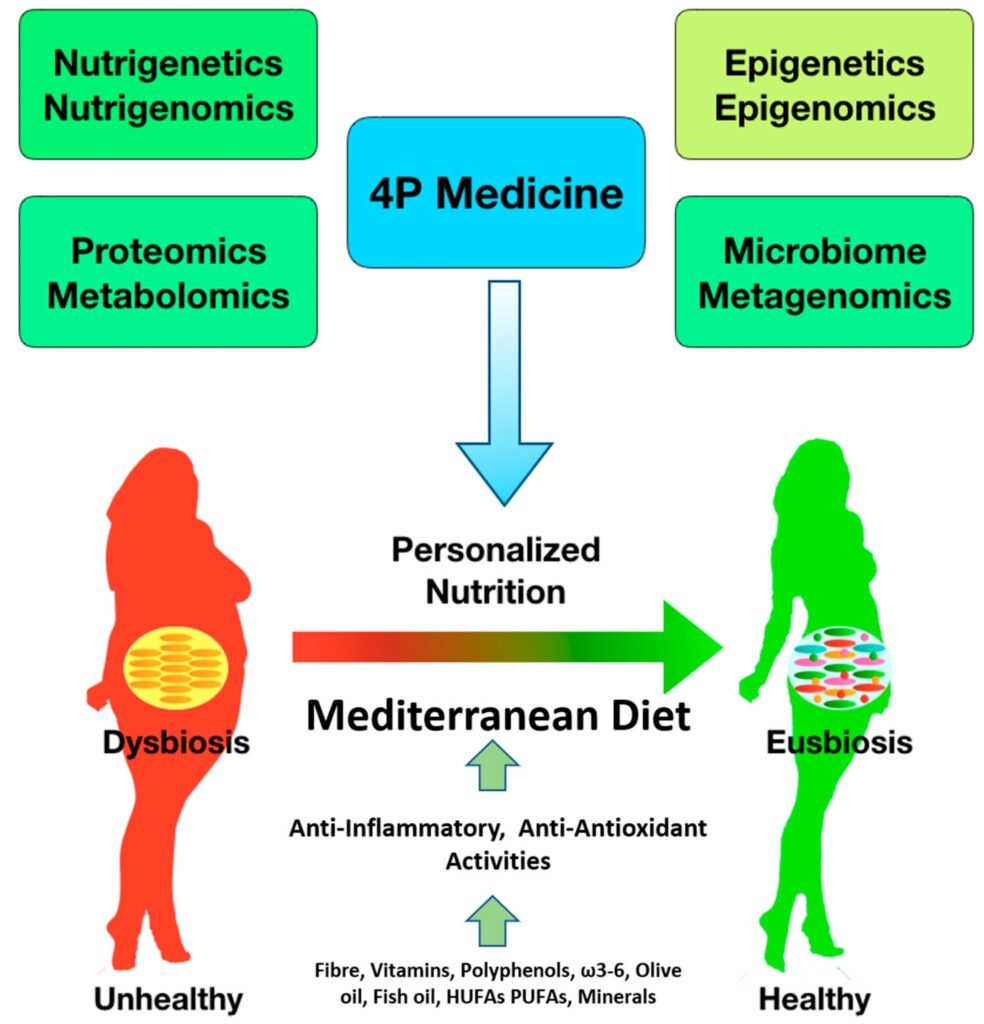
This image is property of www.mdpi.com.
Benefits of Personalized Nutrition
Need for Personalized Nutrition
One size does not fit all when it comes to nutrition. The concept of personalized nutrition recognizes that each individual has unique genetic variations that impact their nutrient requirements, metabolism, and overall health. By tailoring dietary recommendations based on an individual’s genetic makeup, personalized nutrition can help optimize nutrient intake, prevent nutritional deficiencies, and address specific health concerns, leading to improved overall well-being.
Examples of Personalized Nutrition Approaches
There are several personalized nutrition approaches that utilize nutrigenomics to provide tailored dietary recommendations. One example is the analysis of genetic variations related to caffeine metabolism. People with specific genetic variations may metabolize caffeine more slowly, making them more sensitive to its effects. Personalized nutrition guidance for individuals with these variations may emphasize limiting caffeine intake to avoid potential adverse effects.
Another example is the analysis of genetic variations related to lactose intolerance. Some individuals have genetic variations that affect their ability to produce lactase, the enzyme responsible for digesting lactose, the sugar found in milk. Personalized nutrition recommendations for individuals with lactose intolerance-related genetic variations may involve avoiding or limiting dairy products to manage symptoms and ensure optimal nutrient intake.
Reducing Disease Risk through Personalized Nutrition
Personalized nutrition can play a crucial role in reducing the risk of developing chronic diseases. By identifying genetic variations associated with an increased risk of specific conditions, such as heart disease or type 2 diabetes, personalized nutrition can provide targeted dietary recommendations to mitigate these risks. For example, individuals with genetic variations associated with a higher risk of heart disease may benefit from personalized recommendations that prioritize a heart-healthy diet, which includes reducing intake of saturated fats and increasing consumption of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
Understanding Genetic Variants related to Nutrition
Prevalence of Genetic Variants Related to Nutrition
Research has shown that genetic variations related to nutrition are quite prevalent in the general population. For example, approximately 70% of the population carries at least one genetic variant associated with altered nutrient metabolism or utilization. These genetic variations can influence an individual’s nutrient requirements, tolerances, and overall response to diet.
Impact of Genetic Variants on Individual Nutrition Needs
Genetic variants related to nutrition can have a significant impact on an individual’s specific nutrient needs. For example, certain genetic variations may increase the need for specific vitamins or minerals to compensate for impaired absorption or metabolism. Understanding these genetic variations allows healthcare professionals to provide tailored dietary advice to ensure optimal nutrient intake and prevention of related deficiencies or health issues.
Examples of Common Nutrient-related Genetic Variants
There are many well-known genetic variations related to nutrient metabolism and utilization. One example is the MTHFR gene variant, which affects the metabolism of folate, a vital B-vitamin. Individuals with this genetic variant may have reduced enzyme activity, leading to impaired folate metabolism and potentially increased risk of neural tube defects and other health issues. Personalized dietary recommendations for individuals with this variant may include higher intakes of natural food sources of folate or the use of methylated forms of folate supplements.
Another example is the FTO gene variant, which has been linked to an increased risk of obesity. This variant is thought to influence appetite regulation and energy expenditure. Understanding an individual’s FTO gene status can help inform personalized dietary recommendations focused on weight management, such as modulating the macronutrient composition of the diet and promoting regular physical activity.

This image is property of d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net.
Application of Nutrigenomics in Personalized Nutrition
Nutrigenomic Testing Methods
Nutrigenomic testing involves analyzing an individual’s genetic variations related to nutrition using specialized genetic testing methods. These tests typically require a DNA sample, which can be collected through a simple cheek swab or a blood sample. The genetic information obtained through these tests is then analyzed to identify specific genetic variations that impact nutrient metabolism and utilization.
Interpreting Nutrigenomic Test Results
Interpreting nutrigenomic test results requires expertise and knowledge in the field of nutrigenomics. Healthcare professionals trained in nutrigenomics can analyze an individual’s genetic variations and provide personalized dietary recommendations based on the specific genetic profile. They take into account the individual’s unique genetic variations, health goals, and nutritional needs to develop a personalized approach to nutrition.
Creating Personalized Diet Plans based on Nutrigenomics Results
Once nutrigenomic test results are interpreted, healthcare professionals can help individuals create personalized diet plans that align with their genetic profile. These personalized diet plans take into account an individual’s nutrient requirements, metabolic capabilities, and specific health concerns. By tailoring the diet to the individual’s genetic makeup, optimal nutrient intake can be achieved, leading to improved overall health and well-being.
Benefits of Nutrigenomics
Quantifying the Benefits of Nutrigenomics
Research has shown several benefits of utilizing nutrigenomics in personalized nutrition approaches. Studies have demonstrated that individuals who receive personalized dietary recommendations based on their genetic profile are more likely to adhere to these recommendations and achieve their health goals. Furthermore, personalized nutrition has been shown to reduce the risk of chronic diseases and improve overall health outcomes compared to a one-size-fits-all approach.
Direct Benefits of Individualized Nutrition Planning
Individualized nutrition planning based on nutrigenomics offers several direct benefits. It allows individuals to optimize their nutrient intake based on their unique genetic variations, leading to improved nutrient absorption, utilization, and overall health. Personalized nutrition can also help identify and manage specific nutritional deficiencies or intolerances that may otherwise go unnoticed, reducing the risk of related health issues.
Long-term Outcomes of Utilizing Nutrigenomics in Personalized Nutrition
The long-term outcomes of utilizing nutrigenomics in personalized nutrition are promising. By tailoring dietary recommendations based on an individual’s genetic makeup, the risk of developing chronic diseases can be reduced, leading to improved long-term health outcomes. Additionally, personalized nutrition can help improve weight management, optimize athletic performance, and enhance overall well-being. Continued research and advancements in nutrigenomics are expected to further enhance the long-term benefits of personalized nutrition.

This image is property of www.eurekaselect.com.
Limitations and Challenges of Nutrigenomics
Scientific Challenges in Nutrigenomics
While nutrigenomics has shown immense potential, there are still scientific challenges that need to be addressed. Nutrigenomics research is complex and requires large-scale studies to validate findings and establish robust associations between genetic variations and nutrient response. Additionally, the field of nutrigenomics is still relatively new, and there is still much to learn about the interactions between genes and nutrients.
Ethical Concerns in Personal Genomics
The use of personal genomic information raises ethical concerns related to privacy, confidentiality, and discrimination. Genetic information obtained through nutrigenomic testing can reveal sensitive information about an individual’s health risks and predispositions. It is essential to ensure that appropriate safeguards are in place to protect individuals’ privacy and prevent misuse of genetic information.
Potential Misuse of Genetic Information
There is also a risk of the potential misuse of genetic information obtained through nutrigenomics. Genetic information should be used responsibly and only for its intended purpose, which is to provide personalized dietary recommendations and promote health. Clear regulations and ethical guidelines should be in place to prevent the misuse of genetic information for discriminatory or unethical purposes.
The Future of Nutrigenomics and Personalized Nutrition
Emerging Trends in Nutrigenomics
As nutrigenomics research advances, several emerging trends are expected to shape the field. One trend is the incorporation of AI and machine learning technologies to analyze large amounts of genetic and nutritional data more efficiently. This can lead to more accurate and precise personalized dietary recommendations. Another trend is the integration of nutrigenomics into digital health platforms, making personalized nutrition more accessible and convenient for individuals.
Predicted Advancements in Personalized Nutrition
Advancements in personalized nutrition are expected to continue to increase in the coming years. Nutrigenomics research is likely to uncover more genetic variations related to nutrition and their implications for health. This knowledge will enable more precise and targeted dietary recommendations tailored to an individual’s genetic profile. The integration of nutrigenomics with other health-related data, such as microbiome analysis and wearable technology, holds promise for even more personalized and comprehensive approaches to nutrition.
The Potential Impact of Nutrigenomics on Society
The potential impact of nutrigenomics on society is significant. By providing personalized dietary recommendations based on an individual’s genetic profile, nutrigenomics has the potential to improve population health outcomes and reduce the burden of chronic diseases. It can empower individuals to take control of their health by making informed dietary choices, leading to increased overall well-being and quality of life. However, it is essential to ensure equitable access to nutrigenomic testing and personalized nutrition services to avoid exacerbating health disparities.

This image is property of media.springernature.com.
Practical Tips for Embracing Nutrigenomics
Choosing a Genetic Test
When considering nutrigenomic testing, it is essential to choose a reputable and reliable provider. Look for testing companies that have a proven track record in genetic analysis and interpretation. Consider factors such as the accuracy of their genetic testing methods, adherence to privacy and confidentiality standards, and the availability of qualified healthcare professionals to help interpret the results.
Interpreting and Applying Nutrigenomics Test Results
Interpreting nutrigenomics test results can be complex, especially without expert guidance. It is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional trained in nutrigenomics who can accurately interpret the results and provide personalized dietary recommendations based on the specific genetic variations identified. They can help you understand how your genetic makeup influences your nutrition needs and guide you in implementing dietary changes to optimize your health.
Consulting with Healthcare Providers about Nutrigenomics
To fully embrace nutrigenomics and personalized nutrition, it is essential to involve healthcare providers in the process. A healthcare professional trained in nutrigenomics can provide valuable guidance and support throughout your personalized nutrition journey. They can help you understand the implications of your genetic variations, develop a personalized dietary plan, and monitor your progress over time.
Concluding Thoughts
In conclusion, nutrigenomics offers a promising approach to personalized nutrition based on an individual’s genetic makeup. By understanding how specific genetic variations interact with nutrients, personalized dietary recommendations can be developed to optimize health outcomes and reduce the risk of chronic diseases. While there are still challenges to overcome, the future of nutrigenomics and personalized nutrition is bright, with emerging trends and advancements expected to enhance the field further. By embracing nutrigenomics and working with qualified healthcare professionals, individuals can take proactive steps towards achieving optimal health and well-being.
Remember, the field of nutrigenomics is continuously evolving, and further research is needed to better understand the complexities of gene-nutrient interactions. It is essential to stay informed and continue learning as new discoveries shape our understanding of personalized nutrition and its impact on health. If you are interested in exploring nutrigenomic testing and personalized nutrition, reach out to a healthcare professional trained in this field who can guide you on your journey towards optimizing your nutrition and overall well-being.



