Genomics plays a crucial role in public health by illuminating the intricate relationship between genetics and nutrition. This article offers a comprehensive exploration of the field of nutrigenomics, which focuses on understanding how genetic variations affect our responses to diet. By delving into key concepts such as gene-diet interactions, gene expression, and epigenetics, we gain a deeper understanding of how personalized nutrition strategies can optimize health outcomes. With applications ranging from disease prevention and management to performance enhancement, nutrigenomics has the potential to revolutionize our approach to healthcare. However, challenges such as ethical considerations, accessibility, and the complexity of gene-diet interactions must be addressed. By embracing advancements in technology, integrating nutrigenomics into mainstream healthcare practices, and promoting public education and awareness, we can harness the power of genomics to optimize individual health outcomes and pave the way for a healthier future.
This image is property of media.springernature.com.
Overview of Nutrigenomics
Nutrigenomics is a fascinating field of study that explores how genetics influence individual responses to diet. By understanding the intricate relationship between our genes and the food we consume, we can unlock personalized nutrition strategies that optimize our health outcomes. In this article, we will delve into the scope of nutrigenomics, explore the genetic variations that impact our dietary responses, and gain an understanding of the fundamental concepts of gene expression and epigenetics.
Understanding the Scope of Nutrigenomics
Nutrigenomics is the study of how genetic variations affect our responses to certain dietary components. This field combines genetics and nutrition, helping us understand why some people may have different reactions to the same food or nutrient. Through studying the interactions between our genes and diet, we can unravel the underlying mechanisms that dictate individual responses to various nutrients.
Genetic Variations and Dietary Responses
Our genetic makeup plays a crucial role in determining how our bodies process and respond to different nutrients. Certain genes can influence our ability to metabolize specific substances, such as carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. Genetic variations can also affect our sensitivity to certain dietary factors, such as salt or caffeine. By understanding these genetic variations, we can tailor nutritional strategies to meet the unique needs of individuals and optimize their health outcomes.
Introduction to Gene Expression and Epigenetics
Gene expression refers to the process by which information contained within our genes is used to create functional products within our bodies. It involves the transcription of DNA into RNA and the subsequent translation of RNA into proteins. Gene expression can be influenced by various factors, including diet and lifestyle choices.
Epigenetics, on the other hand, studies the modifications to our genes that can occur without changing the underlying DNA sequence. These modifications can be influenced by environmental factors, including diet and stress. Epigenetic changes can impact gene expression and, consequently, our responses to diet. Nutrigenomics seeks to understand these epigenetic modifications and how they can be altered through dietary interventions.
Significance of Nutrigenomics in Personalized Nutrition
The integration of nutrigenomics into personalized nutrition has the potential to revolutionize the way we approach our dietary habits. By tailoring nutritional strategies based on an individual’s genetic profile, we can optimize their health outcomes and reduce the risk of developing chronic diseases. Personalized nutrition takes into account an individual’s unique genetic variations and dietary responses to provide tailored recommendations on food choices, portion sizes, and nutrient intake.

This image is property of blogs.cdc.gov.
Tailored Nutritional Strategies Based on Genetic Profile
One of the key benefits of nutrigenomics is the ability to develop tailored nutritional strategies based on an individual’s genetic profile. By analyzing an individual’s genetic variations, we can identify potential deficiencies or sensitivities to certain nutrients. This information allows us to recommend specific foods or supplements to address these unique needs, ultimately optimizing their health and well-being.
Impact on Individual Health Outcomes
Nutrigenomics plays a crucial role in optimizing individual health outcomes. By considering an individual’s genetic predispositions and dietary responses, we can develop personalized nutrition plans that promote overall health and prevent the onset of chronic diseases. Understanding how our genes interact with the nutrients we consume empowers individuals to make informed choices about their diet, leading to improved health and well-being.
Applications of Nutrigenomics
Nutrigenomics has a wide range of applications beyond personalized nutrition. From optimizing health to preventing and managing diseases, and even enhancing athletic performance, nutrigenomics has the potential to revolutionize various aspects of our lives.
Role in Optimization of Health
By tailoring nutritional plans based on an individual’s genetic profile, nutrigenomics can help optimize overall health and well-being. Understanding how our genes respond to different nutrients allows us to create personalized diets that nourish our bodies in the most effective way possible. This personalized approach can lead to enhanced energy levels, improved cognitive function, and better overall health.
Prevention and Management of Diseases
Another significant application of nutrigenomics is in the prevention and management of diseases. By identifying an individual’s genetic predispositions to certain conditions, such as obesity, diabetes, or cardiovascular diseases, we can develop targeted dietary interventions to reduce the risk of developing these conditions or to manage them more effectively. By optimizing nutrient intake based on genetic variations, we can potentially prevent the onset of chronic diseases and improve the quality of life for individuals.
This image is property of media.springernature.com.
Athletic Performance Enhancement
Nutrigenomics also has the potential to enhance athletic performance. By understanding an individual’s genetic variations, we can tailor nutritional plans to optimize their athletic performance and recovery. This could involve personalized macronutrient ratios, specific nutrient timing strategies, or identifying potential deficiencies or predispositions that could impact performance. Through these personalized approaches, athletes can reach their maximum potential and improve their overall competitive edge.
Ethical Aspects in Nutrigenomics
While the potential benefits of nutrigenomics are vast, it is essential to consider the ethical considerations surrounding its use. The collection and utilization of genetic information in personalized nutrition raise concerns related to privacy, consent, and potential misuse of this sensitive data.
Concerns Regarding Privacy and Consent
As with any field that deals with personal genetic information, there is a need to ensure the privacy and consent of individuals participating in nutrigenomic studies. Safeguarding genetic data requires strict protocols and adherence to ethical guidelines to protect individuals from potential harm or misuse of their genetic information. Strict consent procedures should be in place to ensure transparency and provide individuals with the necessary information to make informed decisions.
Ethical Use of Genetic Information
The responsible and ethical use of genetic information is of utmost importance in nutrigenomics. Genetic data should be utilized only for the intended purpose, namely personalized nutrition interventions. Researchers and healthcare professionals must adhere to ethical standards and ensure the protection of individuals’ genetic information. Proper governance and oversight are necessary to regulate the use of genetic information and prevent any potential misuse or discrimination.
Challenges and Limitations of Nutrigenomics
While nutrigenomics holds immense promise, several challenges and limitations must be considered.
This image is property of blogs.cdc.gov.
Accessibility and Affordability Issues
One significant challenge is the accessibility and affordability of nutrigenomics testing and personalized nutrition services. As the field is still relatively new, these services may be limited to certain populations or socioeconomic classes. It is essential to ensure equitable access to these services so that individuals from diverse backgrounds can benefit from personalized nutrition interventions.
Deciphering Gene-Diet Interactions
Deciphering the intricate interactions between genes and diet is another challenge in the field of nutrigenomics. The relationship between genetics and nutrition involves complex mechanisms that are not yet fully understood. Unraveling the specific gene-diet interactions requires extensive research and the development of sophisticated methodologies. Advancements in technology and research methodologies will be crucial in overcoming this challenge.
Current Research Limitations
There are inherent limitations to current research in nutrigenomics. The field is still in its infancy, and the knowledge gaps and unanswered questions are numerous. Further research is needed to fully comprehend the intricate interplay between genetics and nutrition. Long-term studies and large-scale research projects are necessary to validate and expand on current findings, ensuring that the principles of nutrigenomics can be universally applied.
Future Prospects in Nutrigenomics
The future of nutrigenomics holds exciting prospects for advancements in technology, integration into healthcare, and the potential to revolutionize preventive medicine and wellness programs.
Emerging Technologies and Techniques
Advancements in technology, such as advanced sequencing techniques and artificial intelligence, are poised to transform the field of nutrigenomics. These technologies can help researchers uncover new genetic variations, identify novel gene-diet interactions, and develop more accurate predictive models. By harnessing the potential of emerging technologies, we can further our understanding of nutrigenomics and its applications.
This image is property of www.genome.gov.
Integration of Nutrigenomics in Healthcare
The integration of nutrigenomics into mainstream healthcare practices has the potential to revolutionize preventive medicine and wellness programs. By incorporating genetic information into healthcare strategies, healthcare providers can develop personalized dietary recommendations and interventions to prevent the onset of diseases or manage existing conditions more effectively. Nutrigenomics can become an integral part of healthcare, empowering individuals to take control of their health and well-being.
Revolutionizing Preventive Medicine and Wellness Programs
Nutrigenomics has the potential to revolutionize preventive medicine and wellness programs by offering personalized interventions based on an individual’s genetic profile. By utilizing the insights provided by nutrigenomics, healthcare providers can develop proactive strategies to optimize health outcomes and prevent the occurrence of chronic diseases. This paradigm shift from reactive to proactive healthcare can have a significant impact on public health, leading to improved overall well-being and reduced healthcare costs.
Public Education and Awareness in Nutrigenomics
To fully capitalize on the potential of nutrigenomics, public education and awareness are vital.
Importance of Public Education
Educating the public about nutrigenomics and its implications for personalized health and nutrition is crucial. Increasing awareness and understanding of the field will empower individuals to make informed decisions about their dietary choices and seek out personalized nutrition interventions when appropriate. Public education campaigns, workshops, and educational materials can play a significant role in disseminating accurate and reliable information about nutrigenomics.
Implications for Personalized Health and Nutrition
Understanding nutrigenomics has far-reaching implications for personalized health and nutrition. By incorporating genetic information into dietary recommendations, individuals can optimize their nutrition to meet their unique needs. This personalized approach takes into account an individual’s genetic variations and dietary responses, enabling them to achieve their health goals effectively.
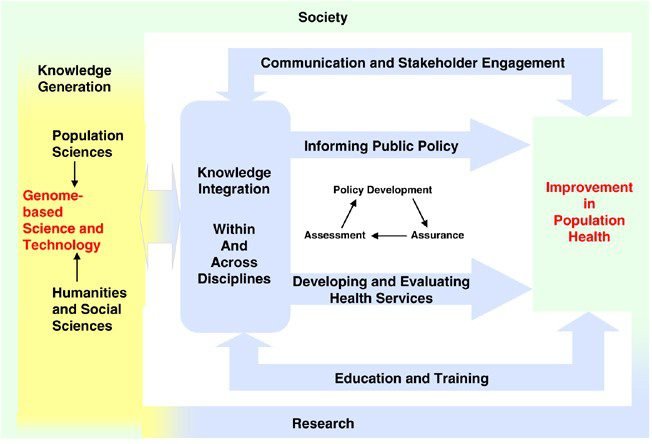
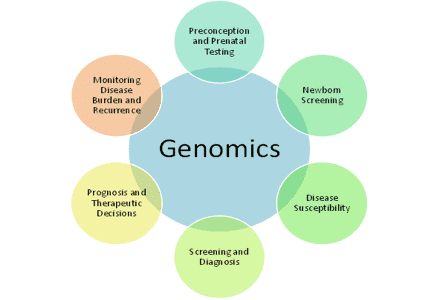
Role of Genomics in Public Health
Genomics plays a vital role in public health, from genetic screening and testing to disease prevention and control, as well as surveillance and response to outbreaks of infectious diseases.
Genetic Screening and Testing
Genetic screening and testing are essential tools in public health. They help identify individuals at risk for certain genetic conditions, enabling early interventions to prevent or manage these conditions. By identifying genetic predispositions, public health agencies can implement targeted interventions and develop strategies for disease prevention and control.
Disease Prevention and Control
Genomics plays a key role in disease prevention and control. By understanding the genetic factors that contribute to disease development, public health agencies can develop targeted interventions for at-risk populations. This approach allows for more effective prevention efforts, as interventions can be tailored to the specific genetic variations that increase an individual’s susceptibility to a particular disease.
Surveillance and Response to Outbreaks of Infectious Diseases
Genomics has proven invaluable in the surveillance and response to outbreaks of infectious diseases. By sequencing the genomes of pathogens, public health agencies can track the spread of diseases, identify sources of infection, and develop appropriate response strategies. Genomic surveillance provides real-time insights into the genetic variations of pathogens, enabling timely and targeted interventions to mitigate the impact of infectious disease outbreaks.
Incorporation of Genomics in Public Health Policies
The incorporation of genomics into public health policies requires careful consideration of ethical and practical considerations.
Formulation of Genetic Policies
The formulation of genetic policies is essential to ensure the responsible and ethical use of genomics in public health. Policies should address issues such as consent, privacy, and the appropriate use of genetic information. Stakeholder engagement is crucial in developing policies that balance the potential benefits and risks associated with genomics and promote public trust.
Ethical Considerations in Policy Making
Public health policies involving genomics should address ethical considerations to protect individuals’ rights and promote accountability. Ethical guidelines should be in place to govern the collection, storage, and use of genetic information, ensuring privacy, consent, and the prevention of discrimination or stigmatization based on genetic characteristics. Policy-making processes should involve a diverse range of stakeholders to ensure that ethical considerations are adequately addressed.
Conclusion
In conclusion, nutrigenomics offers a unique and personalized approach to nutrition by considering an individual’s genetic variations and dietary responses. By understanding the interplay between our genes and the food we consume, we can optimize health outcomes and prevent the onset of chronic diseases. However, there are challenges and limitations that need to be addressed, including ensuring accessibility and affordability, deciphering complex gene-diet interactions, and advancing research methodologies. The future of nutrigenomics holds great promise, with emerging technologies, integration into healthcare, and the potential to revolutionize preventive medicine and wellness programs. It is crucial to educate the public and raise awareness about nutrigenomics to empower individuals to make informed decisions about their health. By incorporating genomics into public health, we can enhance disease prevention and control efforts and respond effectively to outbreaks of infectious diseases. Continued research, education, and integration of nutrigenomics in healthcare are essential for unlocking the full potential of this field and optimizing individual health outcomes.



