The future of nutrigenomics is an exciting new field that explores personalized nutrition through genetic testing. In this article, we will delve into the latest research and discoveries in nutrigenomics, capturing your attention right from the start. With surprising statistics on the prevalence of genetic variants related to nutrition and real-life examples of how this research can be applied, you’ll soon discover the immense potential of personalized nutrition. From discussing the benefits of tailoring diets based on individual genes to providing practical tips on how to learn more about nutrigenomics testing, this article aims to inform and empower health-conscious consumers. So, let’s dive into the world of nutrigenomics and uncover a personalized approach to optimal nutrition.
Understanding Nutrigenomics
Defining Nutrigenomics
Nutrigenomics, also known as nutritional genomics, is a branch of science that explores the relationship between an individual’s genes, their dietary choices, and their health outcomes. It involves understanding how genetic variations can influence an individual’s nutritional needs and how this knowledge can be used to personalize diet and lifestyle recommendations.
History and Development of Nutrigenomics
The field of nutrigenomics has its roots in the intersection of genetics and nutrition, dating back to the discovery of the structure of DNA in the 1950s. Over the years, advancements in technology and genetic research have enabled scientists to delve deeper into the impact of genetics on nutritional requirements.
In the early stages, researchers focused on identifying specific genes and genetic variants that were associated with nutrient metabolism and their role in disease susceptibility. As the field progressed, it became apparent that genetics alone is not the sole determinant of health outcomes, and other factors such as the environment and lifestyle choices also play a significant role.

This image is property of kajabi-storefronts-production.kajabi-cdn.com.
Application of Nutrigenomics today
In recent years, nutrigenomics has gained increased attention and is being applied in various areas of health and wellness. One of the key applications is personalized nutrition, where an individual’s genetic information is used to develop tailored diet and lifestyle recommendations. By understanding the genetic factors that influence an individual’s response to nutrients, personalized nutrition aims to optimize health outcomes and prevent or manage chronic diseases.
Another area where nutrigenomics is playing a crucial role is in the prevention and treatment of diseases. Understanding the genetic variants that contribute to the development of certain conditions allows healthcare professionals to develop targeted interventions, whether through dietary modifications, supplements, or lifestyle changes, to mitigate the risk or progression of these diseases.
Genetics and Nutritional Requirements
Role of Genetics in Determining Nutritional Needs
Genetics plays a significant role in determining an individual’s nutritional needs. Certain genetic variants can affect how the body processes and metabolizes nutrients, impacting nutrient absorption, utilization, and elimination. For example, variations in genes involved in folate metabolism can influence an individual’s requirements for this essential B-vitamin.
By understanding these genetic variations, individuals can personalize their nutritional intake to optimize their health. Nutrigenomics can provide insights into how specific genes impact macronutrient requirements, vitamin and mineral needs, and even dietary sensitivities or intolerances.
Significant Genetic Variants Influencing Nutrition
Numerous genetic variants have been identified that can influence an individual’s nutritional requirements. One well-known example is the MTHFR gene, which codes for an enzyme involved in folate metabolism. Variations in this gene can affect an individual’s ability to convert dietary folate into its active form, potentially increasing the risk of certain health conditions.
Other genetic variants that have been studied include those related to lactose intolerance, caffeine metabolism, and sensitivity to specific nutrients, such as omega-3 fatty acids. By understanding these genetic variations, individuals can make informed choices about their dietary habits and tailor their nutrient intake to their unique genetic profile.
How Genetics can Influence Dietary Responses
Individuals may respond differently to the same diet due to their genetic variations. For example, some individuals may be able to efficiently metabolize and utilize certain nutrients, while others may have a reduced ability to do so. This can influence the effectiveness of dietary interventions and the impact of specific nutrients on health outcomes.
By understanding an individual’s genetic profile, healthcare professionals can identify potential areas of concern or variations that may impact dietary responses. This information can be used to customize diet plans, taking into account an individual’s unique genetic makeup and maximizing the effectiveness of dietary interventions.
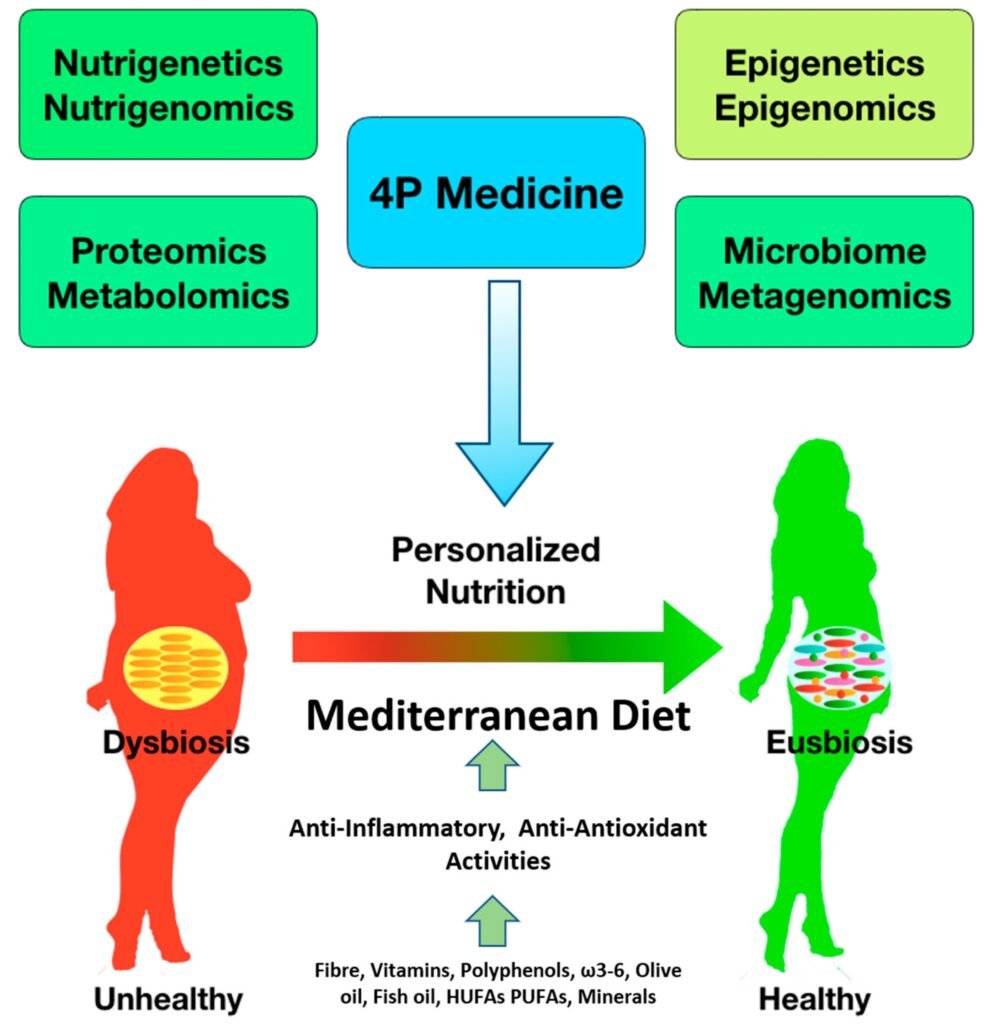
This image is property of www.mdpi.com.
Exploring Personalized Nutrition
Introduction to Personalized Nutrition
Personalized nutrition takes into account an individual’s genetic makeup, along with other factors such as lifestyle and environmental influences, to develop tailored diet and lifestyle recommendations. It recognizes that there is no one-size-fits-all approach to nutrition and that each person has unique needs and responses to dietary factors.
The goal of personalized nutrition is to optimize individual health outcomes by providing personalized dietary recommendations based on an individual’s genetic information. By considering an individual’s genetic variations, healthcare professionals can tailor diet plans to meet specific nutrient needs, address dietary intolerances or sensitivities, and mitigate disease risks.
Benefits of a Personalized Diet
One of the major benefits of personalized nutrition is its potential to improve health outcomes by optimizing nutrient intake and meeting individual needs. By tailoring diet recommendations to an individual’s genetic profile, personalized nutrition can enhance nutrient utilization, reduce the risk of nutrient deficiencies, and potentially prevent the development or progression of certain health conditions.
Another benefit is enhanced dietary adherence. Personalized nutrition takes into account an individual’s preferences, tolerances, and aversions, allowing for the development of diet plans that are more enjoyable and sustainable. By aligning dietary recommendations with an individual’s genetic predispositions, personalized nutrition can increase compliance and promote long-term adherence to healthy eating habits.
Challenges in Personalized Nutrition
While personalized nutrition holds great promise, there are several challenges that need to be addressed. One of the main challenges is the availability and accessibility of genetic testing. Genetic testing is still relatively expensive, and not all individuals have access to these services. Additionally, there is a need for trained healthcare professionals who can interpret genetic data and provide personalized dietary advice based on the results.
Another challenge is the complexity of translating genetic information into practical dietary recommendations. Genetic variations often interact with each other and with environmental factors, making it challenging to establish clear cause-and-effect relationships. Further research is needed to unravel these complexities and develop evidence-based guidelines for personalized nutrition.
Future of Nutrigenomics and Personalized Nutrition
Current Research and Innovations
Advancements in technology and research methodologies have greatly contributed to the progress of nutrigenomics and personalized nutrition. Scientists are currently exploring the potential of epigenetics, which refers to changes in gene expression that are influenced by environmental factors, to further understand the complex interactions between genes and diet.
Another area of ongoing research is the development of biomarkers that can predict an individual’s responsiveness to specific dietary interventions. By identifying biomarkers that correlate with positive health outcomes in response to specific nutrients or dietary patterns, healthcare professionals can refine personalized nutrition recommendations.
Technology’s Role in Expanding Personalized Nutrition
Technology has played a significant role in advancing nutrigenomics and expanding the possibilities of personalized nutrition. Genetic testing has become more accessible and affordable, enabling individuals to obtain valuable insights into their genetic makeup and its implications for nutrition and health.
Furthermore, digital health platforms and mobile applications are emerging that allow individuals to track their diet, lifestyle habits, and health markers. By integrating genetic data with these platforms, individuals can receive personalized feedback and recommendations in real-time, empowering them to make informed choices about their nutrition and overall well-being.
Market potential and Economic Impact
As personalized nutrition gains traction, it has the potential to significantly impact the market for food, supplements, and healthcare services. The ability to tailor diets and nutritional interventions based on an individual’s genetic profile opens up new opportunities for targeted product development and marketing.
However, challenges related to cost-effectiveness, scalability, and data privacy need to be addressed for widespread adoption and integration of personalized nutrition into mainstream healthcare practices. Research efforts and collaborations among academics, healthcare professionals, and industry stakeholders are crucial for overcoming these challenges and realizing the full potential of nutrigenomics in improving population health.

This image is property of media.springernature.com.
Impact of Nutrigenomics on Health
Prevention and Treatment of Diseases
Nutrigenomics has the potential to revolutionize disease prevention and treatment approaches. By understanding the genetic factors that influence disease susceptibility, healthcare professionals can develop targeted interventions to mitigate risks and slow down disease progression.
For example, individuals with genetic variants associated with increased inflammation may benefit from an anti-inflammatory diet to reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as cardiovascular disease and diabetes. By tailoring dietary recommendations to an individual’s genetic profile, nutrigenomics can maximize the effectiveness of interventions and improve long-term health outcomes.
Connection to Weight Management
Weight management is a complex issue influenced by a multitude of factors, including genetics. Several genetic variants have been identified that are associated with body weight, metabolism, and appetite regulation. Understanding an individual’s genetic predispositions related to weight management can help healthcare professionals develop personalized strategies for achieving and maintaining a healthy weight.
By considering an individual’s genetic profile, dietary recommendations can be tailored to address specific challenges in weight management. For example, individuals with genetic variants associated with a higher risk of obesity might benefit from a diet rich in whole foods, high in fiber, and low in added sugars. Nutrigenomics provides valuable insights to develop effective and sustainable weight management strategies.
Contribution to Longevity
Nutrigenomics research has uncovered genetic factors that influence the aging process and longevity. By identifying genetic variations associated with healthy aging, preventive interventions can be developed to promote longevity and improve overall health outcomes in older adults.
For instance, certain genetic variants may affect an individual’s ability to produce antioxidants, which helps protect against oxidative stress. Understanding these genetic variations can guide dietary recommendations, including the consumption of antioxidant-rich foods and supplementation if necessary, to support healthy aging and longevity.
Exploring Genetic Testing and Its Process
Understanding Genetic Testing
Genetic testing involves examining an individual’s DNA to identify specific genetic variants and variations. It provides valuable insights into an individual’s genetic makeup and can help identify potential genetic predispositions to certain diseases, nutrient requirements, and dietary responses.
Genetic testing can be conducted through various methods, including saliva or blood samples, and the samples are analyzed in specialized laboratories. The results provide information about an individual’s genetic variants and can be used to guide personalized nutrition recommendations.
Procedure for Genetic Testing
The process of genetic testing typically involves several steps. First, an individual provides a sample, usually in the form of saliva or blood, which contains their DNA. The sample is then sent to a genetic testing laboratory where it undergoes analysis to identify specific genetic variants.
After the analysis is complete, the laboratory generates a report that outlines the individual’s genetic variations, offering insights into their genetic predispositions relevant to nutrition and health. This report is typically interpreted by a healthcare professional who can provide personalized dietary recommendations based on the results.
Interpretation of Genetic Testing Results
Interpreting genetic testing results requires expertise in genetics and nutrition. A healthcare professional, such as a registered dietitian or genetic counselor, can analyze the genetic variations identified and interpret the implications for an individual’s nutritional needs and dietary responses.
The results of genetic testing can provide valuable information about an individual’s unique nutrient requirements, dietary sensitivities or intolerances, and potential disease risks. The interpretation of these results can guide personalized nutrition recommendations, empowering individuals to make informed choices about their diet and lifestyle.
This image is property of nap.nationalacademies.org.
The Role of Genetic Testing in Personalized Nutrition
Determining Health Risks
One of the primary roles of genetic testing in personalized nutrition is to identify an individual’s genetic predispositions to certain health conditions. By understanding an individual’s genetic risk factors, healthcare professionals can develop targeted interventions to mitigate risks and promote preventive measures.
For example, genetic testing may reveal an increased risk of cardiovascular disease based on specific genetic variants. With this knowledge, healthcare professionals can recommend dietary interventions, such as increasing intake of heart-healthy foods and reducing intake of saturated fats, to help reduce the risk of developing cardiovascular disease.
Identification of Nutritional Needs
Genetic testing provides insights into an individual’s unique nutrient requirements. By identifying genetic variations that influence nutrient metabolism and utilization, healthcare professionals can tailor dietary recommendations to meet an individual’s specific nutritional needs.
For instance, genetic variations in the FADS1 gene have been linked to differences in omega-3 fatty acid metabolism. Individuals with these variations may require higher levels of omega-3 fatty acids from dietary sources or supplements to achieve optimal health outcomes. Genetic testing, therefore, plays a vital role in identifying nutrient deficiencies or requirements that may otherwise go unnoticed.
Formulation of Personal Diet Plans
Personalized nutrition revolves around developing specific diet plans tailored to an individual’s genetic profile. Genetic testing provides valuable information that can shape these personalized diet plans, taking into account an individual’s genetic information and dietary preferences.
By considering an individual’s genetic variations, healthcare professionals can recommend dietary modifications to optimize nutrient intake and address specific needs or sensitivities. For example, individuals with lactose intolerance may benefit from a dairy-free diet, while those with variations related to caffeine metabolism may require adjusted caffeine consumption.
Implementing Personalized Nutritional Advice
Connecting Nutrigenomics and Daily Diet
Implementing personalized nutrition into daily life involves making practical changes to one’s diet and lifestyle based on the insights from genetic testing. It is essential to create a strong connection between nutrigenomics and everyday dietary choices to promote long-term adherence and positive health outcomes.
Developing a personalized nutrition plan involves working with a healthcare professional who is trained in interpreting genetic testing results and translating that information into practical dietary recommendations. These recommendations can include adjusting macronutrient intake, increasing or decreasing specific nutrient consumption, and incorporating personalized guidelines into meal planning.
Roadblocks in Framework Implementation
While personalized nutrition holds great promise, there are roadblocks to its implementation. One significant hurdle is the availability and affordability of genetic testing. Genetic testing is becoming more accessible, but it is still not universally affordable for all individuals. Widespread availability and affordability are essential for the successful integration of personalized nutrition into daily life.
Another challenge is the need for education and expertise among healthcare professionals. To effectively implement personalized nutrition, healthcare professionals need training in understanding and interpreting genetic information. This ensures accurate analysis of genetic testing results and the ability to provide personalized recommendations to their clients.
Future Perspectives of Adapting Personalized Nutrition
The future of personalized nutrition is promising, with ongoing research and technological advancements driving progress. As our understanding of genetics and its impact on nutrition expands, the application of personalized nutrition is expected to become more accessible and practical for individuals.
Emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, are anticipated to play a role in improving the interpretation and analysis of genetic data, making personalized nutrition more accurate and efficient. Additionally, collaborations between researchers, healthcare professionals, and technology companies will facilitate the integration of personalized nutrition into mainstream healthcare systems.

This image is property of adntro.com.
Ethical Considerations and Challenges
Dealing with Genetic Information
Personalized nutrition relies on the use of genetic information to develop tailored diet and lifestyle recommendations. This raises ethical considerations regarding the handling and storage of genetic data. Privacy and security concerns need to be addressed to ensure the protection of individuals’ sensitive genetic information.
Regulations and guidelines are in place to protect individuals’ privacy and prevent misuse of genetic data. Healthcare professionals and researchers are bound by ethical standards to ensure confidentiality and informed consent when working with genetic information. Advances in data encryption and secure storage solutions are continually being developed to safeguard genetic data.
Possibility of Genetic Discrimination
The use of genetic information in personalized nutrition also raises concerns about potential genetic discrimination. Genetic discrimination occurs when individuals are treated unfairly based on their genetic information, such as denial of employment or insurance coverage.
To prevent genetic discrimination, laws and regulations are in place in many countries to protect individuals from such discrimination. These laws prohibit employers and insurance providers from using genetic information to make discriminatory decisions. Promoting awareness and understanding about genetic privacy and non-discrimination laws is crucial to ensure the ethical and responsible use of genetic information.
Regulations Surrounding Genetic Testing
Genetic testing falls under regulatory frameworks that ensure the accuracy and reliability of testing procedures and interpretations. These regulations vary by country, but they generally aim to safeguard the quality and validity of genetic testing services.
Healthcare professionals and individuals seeking genetic testing should be aware of the regulatory landscape and ensure that testing services adhere to the applicable regulations. This includes conducting tests in accredited laboratories and working with healthcare professionals who have the necessary qualifications and expertise in genetic interpretation.
Embracing the Future of Nutrigenomics
Encouraging Genetic Testing for Personalized Nutrition
As the field of nutrigenomics continues to evolve and research advances, encouraging individuals to undergo genetic testing can provide valuable insights into their nutritional needs and health risks. Genetic testing empowers individuals to take a proactive approach to their health by making informed choices about their diet and lifestyle.
Promoting awareness about the benefits and potential of personalized nutrition can increase acceptance and uptake of genetic testing services. Education campaigns, public health initiatives, and collaborations between healthcare professionals and genetic testing companies can help disseminate knowledge and encourage individuals to embrace the future of nutrigenomics.
Exploring Various Genetic Testing Options
There are various genetic testing options available that cater to different needs and preferences. From comprehensive tests that analyze multiple aspects of an individual’s genetic profile to targeted tests that focus on specific genetic variations, individuals have choices when it comes to genetic testing.
It is important to research and choose a reputable genetic testing provider that offers accurate and reliable testing services. Working with a healthcare professional who can interpret the test results and provide personalized recommendations based on the genetic information is also beneficial.
Proposed Action Plans to Integrate Nutrigenomics into Daily Life
To integrate nutrigenomics into daily life, individuals can take several action steps:
Educate Yourself: Learn about the field of nutrigenomics, genetic testing, and personalized nutrition. Stay informed about the latest research and advancements in the field.
Seek Professional Guidance: Consult with a healthcare professional who is knowledgeable in nutrigenomics and personalized nutrition. They can help interpret genetic testing results and provide personalized dietary recommendations.
Consider Genetic Testing: Explore the options for genetic testing and consider undergoing testing to gain insights into your unique genetic profile. Choose a reputable provider and ensure the confidentiality and privacy of your genetic information.
Implement Personalized Recommendations: Incorporate the personalized dietary and lifestyle recommendations provided by your healthcare professional into your daily routine. Make gradual changes and track your progress to assess the impact of personalized nutrition on your health and well-being.
By taking these actions, individuals can embrace the future of nutrigenomics and unlock the potential of personalized nutrition to optimize their health and well-being.
In conclusion, nutrigenomics is an exciting field that offers insights into how an individual’s genetic makeup can influence their nutritional needs and dietary responses. Personalized nutrition based on genetic testing holds great promise in optimizing health outcomes and preventing or managing diseases. Integrating nutrigenomics into daily life requires education, guidance from healthcare professionals, and proactive steps to undergo genetic testing and implement personalized recommendations. By embracing the future of nutrigenomics, individuals can unlock the power of personalized nutrition and take control of their health through informed dietary choices.



