Nutrigenomics, also known as nutritional genomics or nutrigenetics, is a rapidly growing field that explores the interaction between our genes and the foods we consume. By understanding the unique genetic variations that affect how our bodies process and respond to nutrients, researchers are uncovering exciting possibilities for personalized nutrition. This article will delve into the future of nutrigenomics and its impact on personalized nutrition, presenting fascinating research, surprising statistics, and practical tips for implementing a personalized diet based on an individual’s genes. So, if you’re ready to discover how your genes can shape your nutritional needs, read on to learn more about the exciting world of nutrigenomics.
What is Nutrigenomics?
Nutrigenomics is a branch of science that focuses on the interaction between nutrition and genetic variations. It explores how our genes influence our response to different nutrients and how diet impacts gene expression. By understanding this connection, nutrigenomics aims to develop personalized nutrition recommendations for individuals based on their genetic makeup.
Definition of Nutrigenomics
Nutrigenomics, also known as nutritional genomics or genotype-based nutrition, is the study of how our genes interact with the food we eat. It investigates how variations in our genetic code can affect our metabolism, nutrient absorption, and overall health. By analyzing an individual’s unique genetic profile, nutrigenomics seeks to provide personalized recommendations for optimal nutrition and disease prevention.
Relation of Nutrigenomics to Human Genetics
Nutrigenomics is closely linked to the field of human genetics as it investigates the influence of genetic variations on an individual’s response to nutrients. It explores how genetic factors can determine an individual’s risk of developing certain diseases, their susceptibility to nutrient deficiencies, and their ability to metabolize certain compounds found in food. By studying the relationship between genetics and nutrition, nutrigenomics aims to uncover personalized dietary approaches that can promote health and prevent disease.
Key Components of Nutrigenomics
The key components of nutrigenomics include genetics, nutrition, and their interplay. Genetics refers to an individual’s unique genetic makeup, including their DNA sequence and any genetic variations they may have. Nutrition encompasses the food and nutrients that we consume on a daily basis. Nutrigenomics focuses on understanding how an individual’s genetic profile influences their response to different nutrients and how dietary components can impact gene expression. By considering these key components, nutrigenomics aims to provide personalized dietary recommendations for optimal health and well-being.
Understanding the Connection between Genetics and Diet
Role of Genetics in Nutrition
Genetics plays a vital role in how our bodies process and metabolize different nutrients. Certain genetic variations can affect the production and activity of enzymes involved in nutrient metabolism, leading to differences in how individuals respond to specific foods or dietary patterns. For example, some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to lactose intolerance, which affects their ability to digest lactose, a sugar found in dairy products. Understanding an individual’s genetic makeup can help identify potential nutrient deficiencies, intolerances, or sensitivities, and guide personalized dietary recommendations.
Genotype-Diet Interrelationships
Genotype-diet interrelationships refer to the complex interactions between an individual’s genetic profile and their dietary choices. Nutrigenomics aims to elucidate how specific genetic variations can influence how the body processes and utilizes nutrients from food. For example, certain genetic variations may affect an individual’s metabolism of fatty acids, impacting their response to a high-fat diet. By understanding these interrelationships, nutrigenomics seeks to develop tailored dietary recommendations that optimize an individual’s genetic potential for health and well-being.
Evolving Research in the Diet-Genetics Field
The field of diet-genetics research is rapidly evolving, with countless studies shedding light on the complex interactions between our genes and our diet. Advances in technologies such as genome sequencing have made it easier and more affordable to analyze an individual’s genetic profile, allowing for more extensive research in this field. Researchers are uncovering new genetic variations that influence nutrient absorption, metabolism, and response, leading to the development of increasingly personalized dietary recommendations. As this research continues to grow, so does our understanding of how our genes interact with our diet.
This image is property of nap.nationalacademies.org.
Synonyms and Related Terms to Nutrigenomics
Nutritional Genomics
Nutritional genomics is a term used interchangeably with nutrigenomics. It refers to the study of how our genes interact with the nutrients we consume and the impact on our health. Nutritional genomics encompasses both the genetic factors that influence our response to different nutrients and the ability to develop personalized dietary recommendations based on this information.
DietGenomics
DietGenomics is another term that is often used synonymously with nutrigenomics. It combines the words “diet” and “genomics” to emphasize the study of how an individual’s genetic makeup interacts with their dietary choices. DietGenomics aims to understand how our genes influence our nutrient needs and response to different dietary patterns, ultimately guiding personalized nutritional recommendations.
Genotype-based Nutrition
Genotype-based nutrition is a term used to describe the practice of tailoring dietary recommendations based on an individual’s genetic profile. It recognizes that each person’s genetic makeup is unique and that personalized nutrition should account for these genetic variations. By understanding an individual’s genotype, healthcare practitioners can provide them with personalized dietary guidelines that optimize their genetic potential for health.
Advancements in Nutrigenomics Research
Current Findings in Nutrigenomics
Advances in nutrigenomics research have revealed fascinating findings about how our genes interact with our diet. Researchers have identified specific genetic variants that affect an individual’s response to various nutrients, including macronutrients such as carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, as well as micronutrients like vitamins and minerals. This research has also highlighted the impact of genetic variations on the risk of developing certain diseases, such as obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular conditions. By uncovering these current findings, nutrigenomics research paves the way for personalized dietary interventions that can promote health and disease prevention.
Technologies Empowering Nutrigenomics
Technological advancements have played a crucial role in empowering nutrigenomics research. One such advancement is the availability of affordable genetic testing, which allows individuals to uncover their unique genetic variations related to nutrition. With the advent of techniques such as genome sequencing and DNA microarray analysis, researchers can gather comprehensive genetic information and identify specific variations associated with nutrition-related traits. These technologies enable a deeper understanding of how an individual’s genes interact with their diet and guide the development of personalized nutrition recommendations.
Organizations Involved in Nutrigenomics Research
Numerous organizations are involved in nutrigenomics research, aiming to advance our knowledge and application of personalized nutrition. These organizations include academic institutions, research centers, and private companies. Academic institutions such as universities offer dedicated nutrigenomics research programs and centers, where scientists collaborate to unravel the intricate connections between genetics and nutrition. Additionally, private companies are emerging in the field, offering genetic testing services and personalized nutrition advice based on an individual’s genetic profile. The collaboration between these organizations is driving the progress of nutrigenomics research and its application in personalized nutrition.
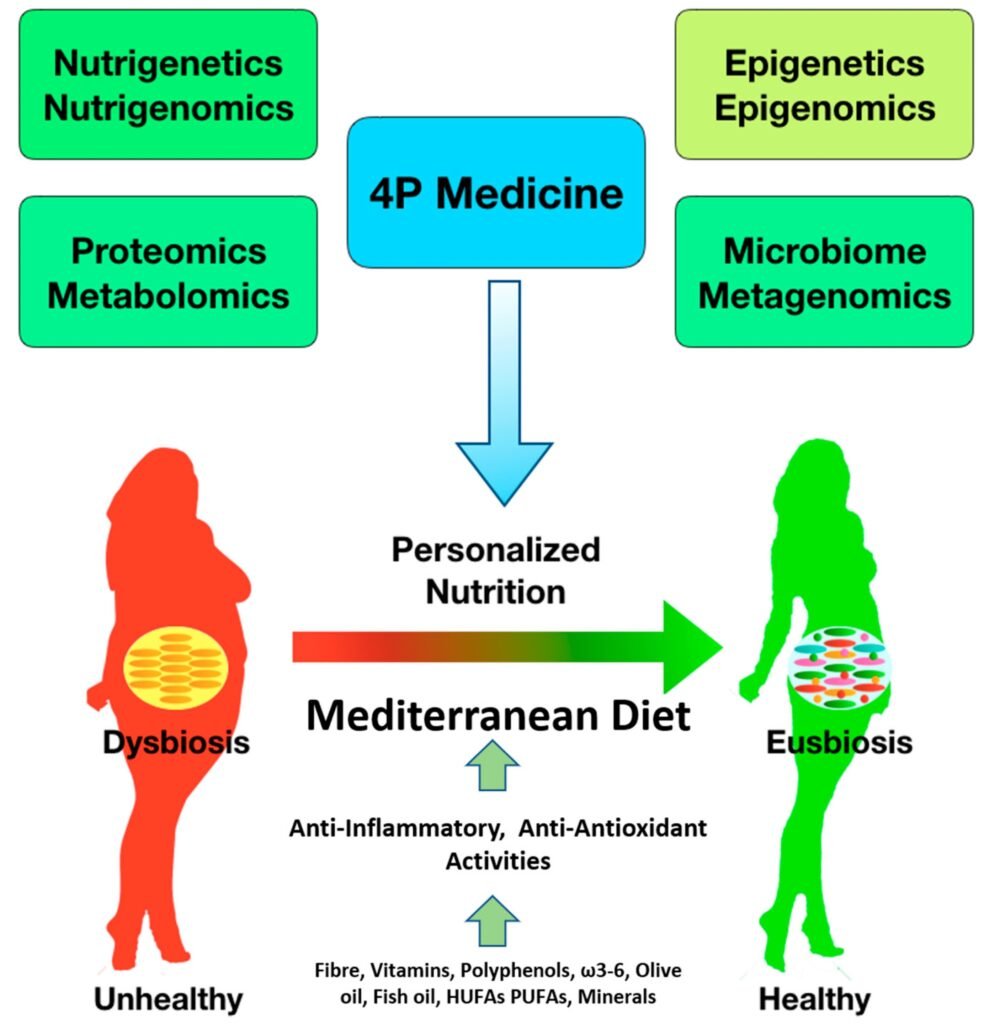
This image is property of www.mdpi.com.
Prevalence of Genetic Variants Related to Nutrition
Common Genetic Variants Affecting Nutrition
Genetic variants related to nutrition are relatively common in the general population. Some of these variants influence how individuals process specific nutrients, such as carbohydrates, fats, and vitamins. For example, a variant in the FTO gene has been associated with an increased risk of obesity and a diminished response to dietary interventions. Another well-known variant is the MTHFR gene variant, which affects the metabolism of folate, an essential B-vitamin. These common genetic variants can have a significant impact on an individual’s response to diet and should be taken into account when developing personalized nutrition strategies.
Impact of Genetic Variants on Personal Health and Nutrition
Genetic variants related to nutrition can have a profound impact on an individual’s personal health and nutrition. Certain genetic variations can increase the risk of developing specific health conditions or affect the body’s ability to metabolize certain nutrients effectively. For instance, individuals with variations in the lactase gene may experience lactose intolerance, leading to digestive discomfort after consuming dairy products. Other genetic variants may impact an individual’s nutrient absorption or utilization, potentially leading to nutrient deficiencies or imbalances. Understanding the impact of these genetic variants is crucial in developing personalized nutrition approaches that optimize health and well-being.
Statistics on Prevalence of such Genetic Variants
The prevalence of genetic variants related to nutrition varies depending on the specific variant and the population being studied. For example, the FTO gene variant associated with obesity is estimated to be present in around 30-40% of the general population. The MTHFR gene variant, on the other hand, is estimated to affect approximately 50% of the global population, with varying frequencies observed in different regions and ethnic groups. These statistics highlight the significance of genetic variants in nutrition and emphasize the need to consider personalized nutrition based on an individual’s genetic profile.
Benefits of Personalized Nutrition
Individualized Diet Based on Genetics
One of the significant benefits of personalized nutrition is the ability to tailor dietary recommendations based on an individual’s genetic profile. By considering an individual’s unique genetic variations, personalized nutrition takes into account their specific nutrient needs, tolerances, and sensitivities. It recognizes that not all diets are suitable for everyone and that genetic variations influence how individuals respond to different dietary patterns. Designing an individualized diet based on genetics can optimize nutrient utilization, prevent nutrient deficiencies, and promote overall health and well-being.
Improved Health Outcomes with Personalized Nutrition
Personalized nutrition has the potential to improve health outcomes by addressing individualized needs and genetic variations. By implementing dietary recommendations that are tailored to an individual’s genetic profile, personalized nutrition can optimize nutrient absorption, metabolism, and overall health. For example, individuals with a genetic predisposition to diabetes can benefit from personalized dietary interventions that focus on blood sugar control and insulin sensitivity. By customizing nutrition plans to address specific genetic variants or risks, personalized nutrition can lead to improved health outcomes and a reduced risk of developing chronic diseases.
Prominent Success Cases of Personalized Nutrition
Several success cases highlight the potential benefits of personalized nutrition. One notable example is the work done in individuals with phenylketonuria (PKU), a genetic disorder that affects the metabolism of the amino acid phenylalanine. Through personalized dietary interventions, individuals with PKU can avoid foods high in phenylalanine and consume specialized formulas or low-protein diets. This tailored approach allows individuals with PKU to manage their condition effectively and avoid the adverse effects of phenylalanine accumulation. Such success cases demonstrate the power of personalized nutrition in optimizing health outcomes for individuals with specific genetic variations or metabolic disorders.

This image is property of d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net.
Challenges and Limitations of Nutrigenomics
Limitations in Current Research
While nutrigenomics holds great promise, there are limitations to the current research in the field. One limitation is the complex nature of gene-diet interactions, as multiple genes and environmental factors can influence an individual’s response to nutrients. Additionally, the impact of genetic variations on nutrition-related traits is often subtle and may vary among individuals, making it challenging to draw definitive conclusions. The research also requires large and diverse study populations to establish robust associations between genetic variants and dietary response, presenting logistical challenges. Further research is needed to address these limitations and enhance our understanding of nutrigenomics.
Ethical Challenges in Nutrigenomics
The use of genetic information in nutrigenomics raises ethical concerns related to privacy, consent, and potential stigmatization. Genetic data is sensitive and personal, requiring strict safeguards to protect individuals’ privacy and prevent misuse of their information. Additionally, ensuring informed consent is obtained from individuals who undergo genetic testing is crucial to respect their autonomy and empower them to make informed decisions about their health. Another ethical consideration is the potential for genetic information to lead to discrimination or stigmatization based on an individual’s genetic profile. Safeguarding against these ethical challenges is essential in the responsible application of nutrigenomics.
Scientific and Technical Challenges
The field of nutrigenomics faces scientific and technical challenges that limit its widespread application. One challenge is the need for comprehensive and accurate databases linking genetic variations to nutrition-related traits. While significant progress has been made in identifying genetic variants, there is still much to learn about their functional significance and how they interact with diet. Additionally, developing robust and reliable biomarkers for dietary response and health outcomes is a technical challenge in nutrigenomics research. Overcoming these scientific and technical challenges will pave the way for more precise and effective personalized nutrition interventions.
Nutrigenomics Testing for Personalized Diet Advice
Process of Genetic Testing for Nutrition
Genetic testing for nutrition involves analyzing an individual’s genetic profile to identify specific variations related to nutrient metabolism or dietary response. The process typically begins with collecting a DNA sample, often through a saliva or blood sample. The DNA is then analyzed using specialized techniques such as genome sequencing or DNA microarray analysis. The resulting genetic data is compared to established databases linking genetic variations to nutrition-related traits, allowing for personalized diet advice based on the individual’s genetic profile. Genetic testing for nutrition can provide valuable insights into nutrient needs, intolerances, and optimal dietary patterns.
Companies and Products offering Nutrigenomics Testing
Several companies and products offer nutrigenomics testing services, allowing individuals to gain insights into their genetic variations related to nutrition. These services typically involve providing a DNA sample, either through a saliva collection kit or a blood test, which is sent to a laboratory for analysis. The laboratory then generates a report that outlines the individual’s genetic variants and provides personalized dietary recommendations based on the findings. Companies such as 23andMe, DNAFit, and Nutrigenomix are prominent players in the nutrigenomics testing market, offering various levels of genetic analysis and personalized nutrition advice.
Considerations before opting for such testing
Before opting for nutrigenomics testing, there are several considerations individuals should keep in mind. Firstly, it is crucial to understand that the field of nutrigenomics is still evolving, and the information provided by genetic testing for nutrition should be evaluated in the context of current scientific knowledge. Additionally, individuals should be prepared for the potential emotional or psychological impact of uncovering genetic information, as the results may reveal a predisposition to certain health conditions or dietary sensitivities. Moreover, individuals should carefully review the privacy and security measures implemented by the testing company to protect their genetic data. Consulting with a healthcare professional knowledgeable in nutrigenomics can provide individuals with guidance and support in making informed decisions about genetic testing for personalized diet advice.

This image is property of www.eurekaselect.com.
The Future of Nutrigenomics
Predicted Advancements in Nutrigenomics
The future of nutrigenomics holds exciting possibilities for the field of personalized nutrition. As our understanding of genetics and nutrition improves, we can expect advancements in identifying additional genetic variations related to nutrient metabolism and dietary response. Genomic technologies and bioinformatics will become more sophisticated, allowing for more comprehensive analyses and precise recommendations. Furthermore, advancements in our understanding of the microbiome and its interactions with genetics and nutrition will contribute to a more holistic approach to personalized nutrition. These predicted advancements will pave the way for more accurate and effective personalized nutrition interventions.
Effect on Healthcare and Nutrition Industries
The impact of nutrigenomics on the healthcare and nutrition industries is expected to be significant. The integration of personalized nutrition into healthcare practices has the potential to revolutionize disease prevention and management. Healthcare providers may utilize genetic information to develop tailored dietary interventions, minimizing the risk of chronic diseases and improving patient outcomes. The nutrition industry will likely follow suit, offering more personalized dietary products and services based on an individual’s genetic profile. As the awareness and application of nutrigenomics grow, we can expect a shift towards a more personalized and precise approach to healthcare and nutrition.
Impact on Public Health Policies
As nutrigenomics research advances and its potential is realized, it is likely to influence public health policies. Governments and public health organizations may incorporate personalized nutrition strategies into their guidelines, recognizing the importance of genetic variations in shaping dietary recommendations. Policies promoting genetic testing for nutrition-related traits and providing access to personalized nutrition advice may emerge to empower individuals in managing their health. By integrating nutrigenomics into public health policies, governments can promote preventive care and reduce the burden of diet-related chronic diseases on society.
Taking Action: Exploring Personalized Nutrition Options
Steps to Learning More about Nutrigenomics
Interested individuals can take several steps to learn more about nutrigenomics and its application to personalized nutrition. Exploring reputable scientific literature and publications can provide a comprehensive understanding of the field’s current research and future prospects. Additionally, attending conferences or webinars focused on nutrigenomics and personalized nutrition can offer insights from experts in the field. Engaging with healthcare professionals knowledgeable in nutrigenomics and genetics can provide personalized guidance and recommendations based on an individual’s unique genetic profile. By taking these steps, individuals can deepen their knowledge and make informed decisions about incorporating personalized nutrition into their lifestyle.
Choosing the Right Genetic Test
When considering genetic testing for personalized nutrition, it is essential to choose the right test that meets individual needs and preferences. Assessing the scope of genetic analysis offered by different testing companies is crucial, as some may focus solely on nutrition-related traits, while others provide a broader range of health-related insights. Evaluating the credibility and reputation of the testing company, including their scientific expertise and data privacy measures, is also important. Additionally, considering the cost and convenience of the testing process can help individuals choose the test that aligns best with their budget and preferences. Consulting with healthcare professionals familiar with nutrigenomics testing can provide valuable guidance in selecting the right genetic test.
Implementing Personalized Dietary Changes
Implementing personalized dietary changes based on genetic information requires careful consideration and guidance. It is important to remember that genetic variations are just one piece of the puzzle, and a comprehensive approach to personalized nutrition should also account for other factors such as lifestyle, medical history, and individual preferences. Consulting with registered dietitians or certified nutritionists who specialize in personalized nutrition can provide individuals with customized meal plans and practical strategies to integrate genetic insights into their diet. Additionally, monitoring and evaluating the effectiveness of personalized dietary changes with regular health assessments can help individuals track their progress and make adjustments as needed.
In summary, nutrigenomics is an exciting field that explores the interaction between genetics and diet. By understanding how our genetic variations influence our response to different nutrients, nutrigenomics offers the potential for personalized dietary recommendations and improved health outcomes. Genetic testing for nutrition-related traits can provide valuable insights, but it is essential to consider the limitations, ethical implications, and scientific advancements in the field. The future of nutrigenomics holds promise for advancements in personalized nutrition, impacting healthcare practices, nutrition industries, and public health policies. Taking action to learn more about nutrigenomics and exploring personalized nutrition options can empower individuals to optimize their health based on their unique genetic profile.



