“The Future of Nutrigenomics: A Comprehensive Guide” explores the exciting field of personalized nutrition through the lens of Nutrigenomics. With captivating new research highlighting the impact of genetic variants on nutrition, this article aims to grab the attention of health-conscious consumers. By providing surprising statistics and practical examples of how this research can be applied, readers will develop a keen interest in understanding how their genes influence their dietary needs. The article then delves into the benefits of personalized nutrition, emphasizing the importance of tailor-made diet advice based on individual genetic makeup. By offering clear and practical tips on Nutrigenomics testing and implementing personalized dietary recommendations, this comprehensive guide empowers readers to take action towards optimizing their health. Concluding with a summary and a call-to-action to learn more about genetic testing options, this article serves as a valuable resource for anyone eager to explore the future of personalized nutrition.
Understanding Nutrigenomics
Concept of Nutrigenomics
Nutrigenomics is a field of study that explores the interactions between our genes and the nutrients we consume. It focuses on how different dietary components can affect our gene expression and metabolism. By understanding these interactions, researchers aim to develop personalized nutrition approaches that can optimize health and prevent diseases.
Nutrigenomics versus traditional nutritional science
Traditional nutritional science has provided us with valuable information about the general effects of certain foods and nutrients on our overall health. However, nutrigenomics takes this understanding to a whole new level by considering the individual genetic variations that influence how our bodies respond to specific dietary components.
Unlike traditional nutritional science, nutrigenomics recognizes that each person’s genetic makeup plays a crucial role in determining their unique response to various foods. This personalized approach allows for tailored dietary recommendations based on an individual’s genetic composition, contributing to better health outcomes.
The relevance of studying gene-diet interaction
Studying the interaction between genes and diet is essential because it can help us understand why individuals respond differently to the same dietary interventions. By identifying specific genetic variants that affect nutrient metabolism and other biological processes, researchers can gain insights into the underlying mechanisms behind these variations.
Understanding gene-diet interactions can also help identify individuals who may be at a higher risk of certain nutrient deficiencies or diseases. By assessing an individual’s genetic profile, healthcare professionals can provide personalized dietary recommendations that may prevent or mitigate the negative effects of genetic variations on health.
Advancements in Nutrigenomics Research
Latest discoveries in the field of Nutrigenomics
Nutrigenomics research has made significant advancements in recent years, providing exciting insights into how our genes influence our response to various nutrients. One such discovery is the identification of specific genetic variants that affect an individual’s ability to metabolize certain nutrients.
For example, researchers have found that variations in the FTO gene are associated with increased susceptibility to obesity. Individuals with these genetic variants may be more responsive to dietary interventions, such as reducing their intake of high-calorie foods, to manage their weight effectively.
Another exciting development in nutrigenomics research is the identification of genetic variants that influence micronutrient metabolism. For instance, variants in the MTHFR gene can affect the body’s ability to convert folate into its active form. Knowing this, healthcare professionals can recommend an appropriate level of folate intake or suggest alternative sources to support optimal nutritional status in individuals with these variations.
How nutrigenomics is revolutionizing nutritional science
Nutrigenomics has the potential to revolutionize nutritional science by bringing a personalized approach to the forefront. By considering an individual’s genetic makeup, nutrigenomics allows for tailored recommendations that can optimize nutrition and overall health outcomes.
Traditional nutritional recommendations, although helpful for the general population, do not take into account the unique genetic variations that impact nutrient metabolism. Nutrigenomics research aims to fill this gap by providing targeted guidance based on an individual’s genetic profile. This personalized approach can lead to more effective dietary interventions and better outcomes for individuals seeking to improve their health and well-being.
This image is property of nap.nationalacademies.org.
Prevalence of Genetic Variants Related to Nutrition
Statistics on genetic variants
Genetic variants related to nutrition are more common than we might expect. Research suggests that up to 80% of individuals have at least one genetic variation that affects their nutrient metabolism or response to specific foods.
For example, the MTHFR gene variant, which affects folate metabolism, is estimated to be present in approximately 30-50% of the population. Similarly, variations in the FADS1 and FADS2 genes, which impact omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acid metabolism, are present in around 40-50% of individuals.
The prevalence of these genetic variants highlights the importance of considering individual genetic profiles when providing dietary recommendations to optimize nutrition and health.
Impact of these variants on dietary habits
Genetic variations can influence an individual’s dietary habits by affecting their response to certain foods. For example, individuals with genetic variants associated with reduced lactase activity may experience lactose intolerance and, therefore, avoid dairy products.
Similarly, individuals with variations related to bitter taste perception may have a preference for sweet foods. Understanding these genetic influences on dietary habits can help tailor nutrition recommendations to better align with an individual’s taste preferences and metabolic needs.
Recognizing the impact of genetic variants on dietary habits also highlights the importance of personalized nutrition approaches that consider an individual’s genetic composition. By understanding these variations, healthcare professionals can provide dietary recommendations that are both effective and enjoyable for the individual.
Application of Nutrigenomics Research
Practical examples of how Nutrigenomics research is applied
Nutrigenomics research has practical applications that can benefit individuals seeking to optimize their nutrition and overall health. One such example is the use of genetic information to guide dietary recommendations for weight management.
By analyzing an individual’s genetic profile, researchers can identify genetic variants associated with increased risk of obesity or reduced response to specific dietary interventions. With this information, healthcare professionals can provide targeted advice, such as recommending a low-fat diet for individuals with variants associated with higher fat absorption.
Another practical application of nutrigenomics research is personalized nutrient recommendations based on an individual’s genetic variations. By understanding an individual’s genetic predisposition to nutrient deficiencies or suboptimal metabolism, healthcare professionals can recommend specific dietary strategies or nutrient supplements to ensure optimal nutritional status.
Long-term effects of applying Nutrigenomics in daily life
Applying nutrigenomics research in daily life can have significant long-term effects on an individual’s health and well-being. By tailoring dietary interventions based on genetic information, individuals can achieve better nutrition and reduce their risk of developing chronic diseases.
For example, personalized nutrition plans can help individuals with genetic variants associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease optimize their nutrient intake to support heart health. By avoiding dietary components that their genetic makeup may predispose them to negatively respond to, such as high levels of saturated fat, individuals can reduce their risk of developing heart-related complications.
In the long term, personalized nutrition based on genetic information can also promote positive lifestyle changes. By understanding that certain dietary patterns may not be as beneficial for them due to their genetic makeup, individuals may be more motivated to modify their eating habits and adopt healthier choices that align with their genetic needs.

This image is property of ars.els-cdn.com.
Benefits of Personalized Nutrition Based on Genes
Effectiveness of a diet based on genetic composition
Personalized nutrition based on an individual’s genetic composition can be more effective compared to a generic, one-size-fits-all approach. By considering an individual’s genetic variants related to nutrient metabolism and response to foods, healthcare professionals can provide targeted dietary recommendations that are tailored to the individual’s needs.
Studies have shown that personalized nutrition based on genetic information can lead to better adherence to dietary interventions and improved health outcomes. By incorporating genetic factors into dietary planning, individuals can achieve better control over their nutrition, which can translate into better weight management, improved metabolic health, and reduced risk of chronic diseases.
How personalized diet contributes to better nutrition and health
A personalized diet that takes into account an individual’s genetic composition can contribute to better nutrition and overall health in various ways.
Firstly, personalized diet recommendations can optimize nutrient intake based on an individual’s specific needs and genetic variations. This can help prevent nutrient deficiencies and support optimal metabolism, ensuring the body functions at its best.
Secondly, a personalized diet can improve dietary adherence and sustainability. When individuals receive dietary recommendations that consider their genetic makeup and taste preferences, they are more likely to enjoy the recommended foods and find it easier to maintain a healthy eating pattern in the long term.
Lastly, personalized nutrition can help identify potential dietary risk factors based on an individual’s genetic profile. By understanding genetic predispositions, individuals can avoid or reduce their intake of foods that their genetic makeup may make them more susceptible to negatively responding to. This can lower the risk of developing diet-related health issues.
Genetic Testing for Personalized Nutrition
The process of genetic testing
Genetic testing is a key component of personalized nutrition. It involves analyzing an individual’s genetic material, typically through a simple saliva or blood sample, to identify specific variations that may impact nutrient metabolism or dietary response.
The process begins with sample collection, which can be done at home or in a healthcare setting. Once the sample is obtained, it is sent to a laboratory where the DNA is extracted and analyzed. The laboratory then generates a report that provides information on the individual’s genetic variations related to nutrition.
Understanding the results of a genetic test
The results of a genetic test can provide valuable insights into an individual’s genetic predispositions related to nutrition. The report typically includes information on specific genetic variants and their associated risks or benefits.
However, it is important to note that genetic testing results should always be interpreted in the context of valid scientific research and in consultation with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian. They will be able to explain the significance of specific genetic variations and guide individuals on how to apply the findings to their dietary choices.
The role of genetic testing in personalized nutrition
Genetic testing plays a crucial role in personalized nutrition by providing individuals and healthcare professionals with valuable information about an individual’s genetic composition. This information can then be used to optimize nutrition and develop personalized dietary recommendations.
By identifying specific genetic variations, genetic testing can help predict an individual’s nutrient metabolism, response to certain dietary interventions, and potential risks for nutrient deficiencies or chronic diseases. Armed with this knowledge, healthcare professionals can tailor diet plans and provide targeted advice to support optimal nutrition and overall health.
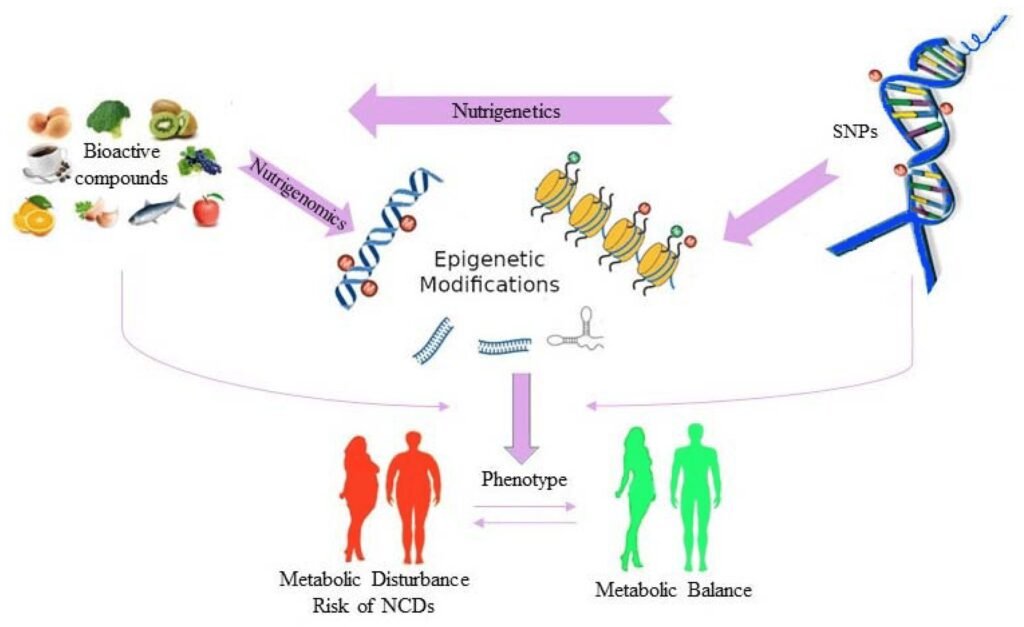
This image is property of pub.mdpi-res.com.
How to Implement Personalized Diet Based on Genetic Composition
Tips to create a diet plan based on genetic information
Implementing a personalized diet based on genetic composition requires careful consideration and guidance from a healthcare professional or registered dietitian. Here are some tips to help create a diet plan based on genetic information:
Seek professional guidance: Consult a healthcare professional or registered dietitian who specializes in nutrigenomics to interpret the results of a genetic test and guide you in developing a personalized diet plan.
Focus on nutrient-dense foods: Emphasize a diet rich in nutrient-dense foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. These foods provide a wide range of nutrients that can support overall health.
Individualize macronutrient ratios: Adjust macronutrient ratios (carbohydrates, fats, and proteins) based on genetic variations that may affect nutrient metabolism. For example, individuals with variants associated with reduced carbohydrate tolerance may benefit from a lower carbohydrate intake.
Pay attention to micronutrient needs: Address specific nutrient needs based on genetic variations that impact nutrient metabolism. For example, individuals with genetic variations affecting vitamin D metabolism may require higher intakes or additional supplementation.
Consider taste preferences: Take into account taste preferences when developing a personalized diet plan. If certain genetic variations influence taste perception, it may be necessary to modify food choices or cooking methods to align with individual preferences.
Challenges in implementing personalized diet and how to overcome them
Implementing a personalized diet based on genetic information may come with certain challenges. It is important to be aware of these challenges and find ways to overcome them:
Limited availability of genetic testing: Access to genetic testing may vary depending on geographical location and healthcare systems. However, with advancements in technology, genetic testing is becoming more accessible. Seek out healthcare professionals or online platforms that offer reliable genetic testing options.
Interpreting complex genetic data: Understanding genetic test results can be complex, requiring specialized knowledge. To overcome this challenge, consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian who specializes in nutrigenomics. They can provide thorough explanations and guide you in applying the findings to your diet plan.
Individual variability: It is important to remember that genetics is just one piece of the puzzle when it comes to overall health. Individual responses to dietary interventions can still vary due to other factors, such as lifestyle, environmental factors, and personal preferences. Taking a holistic approach and considering all these factors is crucial for successful implementation.
Future Trends in Nutrigenomics
Predicted advancements in Nutrigenomics
The field of nutrigenomics is constantly evolving, and several advancements are predicted for the future. Some of the anticipated trends include:
Advancements in genetic testing technology: As technology continues to advance, genetic testing methods are expected to become more accurate, affordable, and accessible, allowing for broader integration of nutrigenomics in healthcare.
Increased research on gene-diet interactions: Further research on gene-diet interactions will likely uncover more specific genetic variations and their impact on nutrient metabolism and dietary response. This knowledge will enhance the development of personalized dietary recommendations.
Integration of nutrigenomics in healthcare systems: As the evidence supporting the benefits of personalized nutrition grows, there is a potential for nutrigenomics to be integrated into mainstream healthcare systems. This could lead to a more widespread adoption of personalized nutrition approaches in clinical practice.
How Nutrigenomics will shape the future of health and nutrition
Nutrigenomics has the potential to shape the future of health and nutrition by providing personalized and targeted approaches to optimize nutrient intake and prevent disease. By considering an individual’s genetic composition, healthcare professionals can tailor dietary recommendations to meet specific needs, supporting overall health and well-being.
As nutrigenomics continues to advance, it holds the promise of revolutionizing the way we approach nutrition and health. By harnessing the power of genetics, we can move towards a future where each individual can achieve optimized nutrition and improved health outcomes.

This image is property of media.springernature.com.
Implication of Nutrigenomics for Health Professionals
How Nutrigenomics can add value in health care delivery
Nutrigenomics can add significant value to health care delivery by providing healthcare professionals with valuable insights into an individual’s genetic predispositions related to nutrition. By integrating nutrigenomics into practice, health professionals can enhance their ability to develop personalized, evidence-based dietary recommendations.
With nutrigenomics, health professionals can identify individuals who may be at a higher risk of nutrient deficiencies or chronic diseases based on their genetic variations. This knowledge allows for targeted interventions that can prevent or mitigate the negative effects of these genetic variations on health.
Training and education needs for health professionals in the field of Nutrigenomics
As nutrigenomics continues to gain recognition and adoption in healthcare settings, there is a need for training and education programs to equip health professionals with the knowledge and skills to effectively utilize nutrigenomics in practice.
Healthcare professionals, including registered dietitians, nutritionists, and physicians, can benefit from specialized training that covers the principles of nutrigenomics, interpretation of genetic testing results, and the application of personalized nutrition strategies.
Ensuring that health professionals have access to proper education and training in nutrigenomics will ultimately enhance their ability to provide evidence-based, individualized dietary recommendations to their patients, leading to improved health outcomes.
Conclusion
The field of nutrigenomics holds tremendous potential for personalized nutrition and optimized health outcomes. By understanding the interaction between our genes and diet, researchers are making exciting discoveries that pave the way for tailored dietary recommendations based on an individual’s genetic composition.
Advancements in nutrigenomics research have already yielded valuable insights into how our genes influence our response to various nutrients and dietary interventions. By incorporating genetic information into dietary planning, individuals can achieve better nutrition, improved metabolic health, and a reduced risk of chronic diseases.
Genetic testing plays a crucial role in personalized nutrition, providing individuals and healthcare professionals with valuable information about an individual’s genetic composition. By considering an individual’s genetic variations related to nutrient metabolism, healthcare professionals can develop targeted dietary recommendations that are tailored to the individual’s needs.
As the field of nutrigenomics continues to grow and evolve, it is important for individuals and healthcare professionals to stay informed and embrace the opportunities it presents. By learning more about genetic testing options and working with healthcare professionals who specialize in nutrigenomics, individuals can take proactive steps towards optimizing their nutrition and overall health.



