Discovering the secrets held within your genes can be a fascinating and empowering experience, especially in the realm of personalized nutrition. However, it is important to recognize that genetic knowledge in this field also comes with its fair share of disadvantages. One of the major drawbacks is the ethical considerations surrounding the use of genetic information, including concerns about privacy and consent. Additionally, the accessibility and affordability of nutrigenomic testing and personalized nutrition services pose significant challenges, limiting their availability to diverse populations. Moreover, the complexity of gene-diet interactions adds another layer of limitation, as current understanding and research methodologies fail to fully decipher the intricate interplay between genes and dietary factors. Despite these disadvantages, the future offers promising opportunities with advancements in technology, integration with healthcare systems, and increased public education and awareness. It is crucial to continue the research, education, and integration of nutrigenomics into healthcare systems and dietary practices, to optimize individual health outcomes and pave the way for a healthier future.
Understanding the Concept and Advantages of Nutrigenomics
Defining Nutrigenomics
Nutrigenomics is a scientific field that focuses on understanding how genetics influence an individual’s responses to diet. By examining the relationship between genes and nutrition, researchers aim to identify the specific genes that affect how the body processes and responds to the nutrients in our food. This information can then be used to develop personalized dietary plans that maximize health outcomes based on an individual’s genetic profile.
Exploring Gene-Diet Interactions
Gene-diet interactions are at the core of nutrigenomics. They refer to the intricate interplay between specific genes and dietary factors, and how these interactions ultimately impact our health. Different individuals may have variations in their genes that affect how their bodies metabolize certain nutrients, making them more or less susceptible to certain health conditions. By studying these gene-diet interactions, scientists can gain insights into how to tailor dietary recommendations to an individual’s unique genetic makeup.
Introduction to Concepts such as Gene Expression and Epigenetics
In order to fully grasp the concept of nutrigenomics, it is important to understand key concepts such as gene expression and epigenetics. Gene expression refers to the process by which information contained within a gene is converted into a functional product, such as a protein. Nutrients in our diet can influence gene expression, either by suppressing or activating certain genes. Epigenetics, on the other hand, is the study of heritable changes in gene function that do not involve changes in the underlying DNA sequence. Epigenetic modifications can be influenced by our diet and lifestyle choices, and can have a significant impact on our health.
Applications of Nutrigenomics: The Benefits
Health Implications of Nutrigenomics
One of the primary benefits of nutrigenomics is its ability to customize dietary plans to optimize health outcomes based on an individual’s genetic profile. By understanding an individual’s genetic variations, healthcare professionals can provide personalized recommendations for nutrient intake, thereby minimizing the risk of nutrition-related diseases. Nutrigenomics can help identify individuals who may have a higher risk for conditions such as obesity, cardiovascular diseases, and diabetes, and develop targeted interventions to prevent or manage these conditions.
Prevention and Management of Diseases through Nutrigenomics
Nutrigenomics holds great potential in the prevention and management of various health conditions. By identifying the specific genetic variations that increase an individual’s susceptibility to certain diseases, healthcare professionals can develop personalized dietary plans that reduce the risk of developing these conditions. Additionally, nutrigenomics can inform targeted interventions for individuals who have already been diagnosed with a particular condition, enabling more effective disease management and improved overall health outcomes.
Abilities of Nutrigenomics to Enhance Performance
In addition to its applications in health and disease prevention, nutrigenomics can also enhance athletic performance. By understanding an individual’s genetic predispositions, healthcare professionals and sports scientists can tailor nutritional strategies to optimize performance and recovery. Nutrigenomics can help identify specific dietary approaches that may boost an athlete’s endurance, strength, and recovery processes. This personalized approach to nutrition can give athletes a competitive edge and contribute to their overall performance improvements.

This image is property of www.mdpi.com.
The Drawbacks of Genetic Knowledge in Personalized Nutrition: An Overview
Introducing the Possible Negative Aspects of Nutrigenomics
While nutrigenomics offers numerous potential benefits, it is important to acknowledge and address the possible drawbacks and challenges associated with genetic knowledge in personalized nutrition. Some of these drawbacks include ethical concerns, access and affordability issues, complexity of gene-diet interactions, overemphasis on genetics, risk of stigmatization and discrimination, and the potential for inaccurate or misleading genetic interpretations. It is crucial to understand these drawbacks in order to develop a balanced and informed perspective on the field of nutrigenomics.
Understanding the Need for an Examination of Risks
As with any field of scientific research and application, it is essential to critically evaluate the risks and limitations associated with the use of genetic knowledge in personalized nutrition. By examining these risks, we can work towards developing ethical guidelines, ensuring accessibility for all, improving research methodologies, and preventing potential harms. This comprehensive examination of risks allows us to move forward in a responsible and sustainable manner, maximizing the benefits while minimizing any potential negative consequences.
Potential Ethical Concerns: Privacy and Consent Issues
Discussing the Ethical Use of Genetic Data in Nutrigenomics
One of the key ethical concerns surrounding nutrigenomics is the issue of privacy and consent. Genetic information is highly personal and sensitive, and its use in personalized nutrition raises questions about the extent to which individuals should have control over their own genetic data. It is important to ensure that individuals have a clear understanding of how their genetic information will be used, who will have access to it, and the potential implications of sharing this information. Safeguarding privacy and obtaining informed consent are essential to maintaining ethical standards in nutrigenomic research and practice.
Understanding the Issues of Privacy and Consent
Privacy and consent issues go hand in hand when it comes to nutrigenomics. Individuals have a right to privacy and autonomy over their genetic information, and it is crucial to establish robust safeguards to protect this information from unauthorized access or misuse. Clear and transparent consent procedures should be implemented, ensuring that individuals are fully aware of how their genetic data will be used and have the autonomy to make informed decisions about its use. Ethical guidelines and regulations should be established to protect individuals’ rights and ensure responsible use of genetic data in personalized nutrition.
Addressing Potential Misuse of Genetic Information
Another ethical concern in nutrigenomics is the potential misuse of genetic information. Genetic data can be used to make predictions about an individual’s health risks or predispositions to certain diseases. However, these predictions are not definitive and should be interpreted with caution. There is a risk of misinterpretation or exaggeration of genetic information, leading to unnecessary anxiety or inappropriate interventions. It is essential to promote responsible and evidence-based use of genetic data, ensuring that it is used in a manner that benefits individuals without causing harm or promoting discrimination.
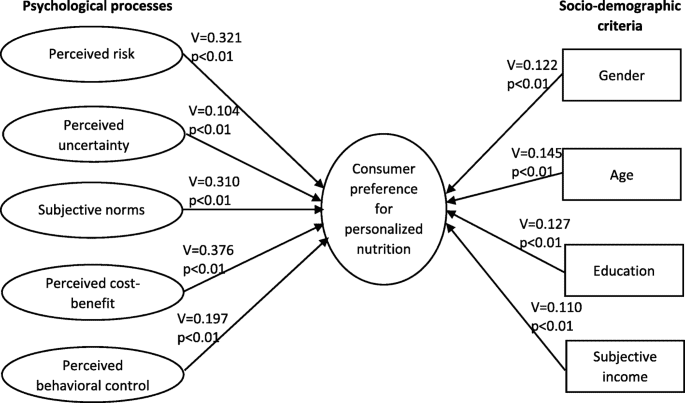
This image is property of media.springernature.com.
Access and Affordability Issues in Nutrigenomics
Analysis of Cost Implications of Genetic Testing
One of the challenges in the widespread implementation of nutrigenomics is the cost associated with genetic testing. Genetic testing involves complex laboratory procedures and data analysis, which can be expensive. This cost can be a barrier to accessing personalized nutrition services for individuals from low-income backgrounds or countries with limited healthcare resources. Addressing the cost implications of genetic testing is crucial for ensuring equitable access to nutrigenomic services and optimizing health outcomes for all individuals.
Disparities in Healthcare Accessibility
In addition to the cost implications of genetic testing, there are disparities in healthcare accessibility that can further hinder the integration of nutrigenomics into personalized nutrition. Not all individuals have equal access to healthcare services, including genetic testing facilities and qualified healthcare professionals who can interpret and provide guidance on the genetic information obtained. Addressing these disparities and ensuring equal access to nutrigenomics is essential to realize the full potential of personalized nutrition in improving health outcomes.
The Economic Challenges of Personalized Nutrition Plans
Implementing personalized nutrition plans based on genetic information can also pose economic challenges. Developing and maintaining the infrastructure required to deliver personalized nutrition services can be costly, both for healthcare providers and individuals seeking these services. Additionally, the development of evidence-based dietary recommendations tailored to an individual’s genetic profile requires ongoing research and data analysis, which requires funding. Finding sustainable economic models to support personalized nutrition plans is necessary to ensure the long-term viability and accessibility of nutrigenomics in the field of healthcare.
The Complexity and Unpredictability of Gene-Diet Interactions
Understanding the Complexities of Gene-Diet Interplay
Despite the promising potential of nutrigenomics, it is important to acknowledge the complexities involved in deciphering gene-diet interactions. The relationship between genes and dietary factors is incredibly intricate, with multiple genes and environmental factors contributing to an individual’s health outcomes. This complexity makes it challenging to pinpoint precise dietary recommendations based solely on genetic variations. Nutrigenomics research is still in its early stages, and further understanding of these complexities is necessary to develop accurate and tailored recommendations for personalized nutrition.
Addressing the Limitations in Current Research Methodologies
Another challenge in nutrigenomics is the limitations in current research methodologies. Studying gene-diet interactions requires large-scale studies with diverse populations over extended periods of time. However, conducting such studies is complex and expensive. Additionally, the interpretation and analysis of data obtained from these studies can be challenging due to the wide range of genetic variations and dietary factors involved. Continual advancements in research methodologies, including the integration of advanced sequencing techniques and artificial intelligence, are needed to overcome these limitations and improve our understanding of gene-diet interactions.
Uncertainties in Predicting Dietary Responses Based on Genetic Variations
Although nutrigenomics aims to personalize dietary recommendations based on an individual’s genetic makeup, it is important to recognize the uncertainties involved in predicting dietary responses. Genetic variations are just one piece of the puzzle, and other factors such as lifestyle, environment, and individual variability can significantly influence how our bodies respond to different diets. The interactions between genes and dietary factors are not always straightforward, and predicting an individual’s response to a particular diet based solely on their genetic variations is still a challenge. Recognizing these uncertainties can help manage expectations and avoid the overreliance on genetic information when developing personalized nutrition plans.
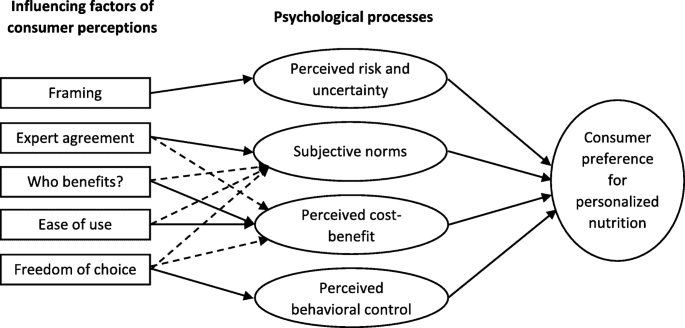
This image is property of media.springernature.com.
The Possibility of Overemphasis on Genetics in Diet
Risks of Disregarding Other Health Factors
While personalized nutrition based on genetic information holds great promise, it is crucial to avoid disregarding other important health factors. Genetics is just one piece of the puzzle when it comes to overall health and nutrition. Factors such as lifestyle choices, environmental influences, socio-economic factors, and cultural preferences all play significant roles in shaping an individual’s dietary needs and health outcomes. Focusing solely on genetics may lead to overlooking these important factors and their impact on overall health and nutrition.
Concerns about an Overreliance on Genetic Information
An overreliance on genetic information in personalized nutrition can also be a cause for concern. While genetic variations can provide valuable insights into an individual’s predispositions and potential risks, they do not provide a complete picture. It is essential to take into account other aspects of an individual’s health, such as current health status, medical history, and dietary habits, in order to develop comprehensive and effective personalized nutrition plans. Relying solely on genetic information may result in overlooking important contextual factors that can significantly impact health outcomes.
Potential Pitfalls in Overlooking Lifestyle and Environmental Factors
Lifestyle and environmental factors are crucial considerations in personalized nutrition, and their importance should not be underestimated. Our dietary choices are not solely determined by our genes but are influenced by various external factors such as cultural practices, societal norms, and food availability. These factors can significantly impact our dietary behaviors and health outcomes. Overlooking lifestyle and environmental factors in favor of a gene-centric approach may not only lead to incomplete dietary recommendations but may also ignore the importance of addressing these external influences to promote sustainable and culturally appropriate dietary changes.
Risk of Stigmatization and Discrimination Based on Genetic Information
Analysis of Potential Stigma Associated with Genotypes
One concerning consequence of personalized nutrition based on genetic information is the risk of stigmatization associated with specific genotypes. Identifying genetic predispositions to certain health conditions may lead to social labeling or categorization based on these genetic traits. Such stigmatization can have negative psychological and social impacts on individuals, potentially leading to discrimination, lower self-esteem, and a reluctance to seek appropriate healthcare. It is essential to mitigate the risk of stigmatization by promoting a holistic and non-judgmental approach to personalized nutrition that focuses on empowerment and improved health outcomes.
Exploring the Possibility of Discrimination Based on Genetic Predispositions
In addition to stigma, there is a concern that knowledge of an individual’s genetic predispositions could lead to discrimination, particularly in areas such as employment or insurance. If genetic information is used as a basis for discrimination, it can have serious ethical and legal implications. Protecting individuals from discrimination based on their genetic information is paramount. Implementing appropriate legal frameworks and regulations that prohibit discrimination based on genetic predispositions is essential to ensure the responsible and ethical use of genetic data in personalized nutrition.
Discussing Societal Consequences of Gene-Centric Attitudes
A gene-centric approach to nutrition can have wider societal consequences. Placing excessive emphasis on genetics may perpetuate the belief that health outcomes are solely determined by an individual’s genetic makeup. This perspective may undermine the importance of addressing social determinants of health and creating equitable access to resources and opportunities for healthy living. A balanced approach that considers both genetic and socio-environmental factors is necessary to promote holistic health and create a more inclusive and fair society.

This image is property of cdn.storymd.com.
Inaccurate or Misleading Genetic Interpretations
Issues with Misinterpretation of Genetic Data
Interpreting genetic data accurately is a complex process that requires expertise and knowledge. Misinterpretation can lead to inaccurate conclusions about an individual’s health risks or nutritional needs, potentially leading to inappropriate dietary interventions. This highlights the importance of ensuring that genetic data is analyzed and interpreted by qualified professionals who have a deep understanding of both genetics and nutrition. Adequate training and accreditation programs should be in place to ensure the accuracy and reliability of genetic interpretations in personalized nutrition.
Potentially Misleading Genetic Reports
The availability of direct-to-consumer genetic testing kits has increased in recent years. While these kits offer individuals the convenience of accessing their genetic information from the comfort of their own homes, there is a risk of potentially misleading genetic reports. Due to the complexity of gene-diet interactions and the limitations of current research, the accuracy and reliability of these reports may vary. Individuals who rely solely on these reports for personalized nutrition may receive misleading recommendations that could negatively impact their health. It is important to ensure that individuals are aware of the limitations and potential inaccuracies of direct-to-consumer genetic testing and seek guidance from qualified healthcare professionals when interpreting and applying genetic information in their dietary choices.
Concerns over Errors in Personalized Diet Recommendations
Errors in personalized diet recommendations can have serious health implications. As the field of nutrigenomics continues to evolve, it is essential to regularly update and refine the guidelines and recommendations based on the latest scientific evidence. Failure to do so could result in outdated or incorrect recommendations being provided to individuals, compromising their health outcomes. Ensuring a strong evidence base and ongoing research is necessary to minimize the risk of errors in personalized diet recommendations and maintain the highest standards of care in the field of nutrigenomics.
Conclusion: Balancing the Benefits and Risks of Genetic Knowledge in Personalized Nutrition
Summary of the Advantages and Disadvantages of Nutrigenomics
In conclusion, nutrigenomics offers significant potential for personalized nutrition and improved health outcomes. Through understanding gene-diet interactions and utilizing genetic information, personalized dietary plans can be developed to optimize health, prevent disease, and enhance performance. However, it is important to recognize and address the drawbacks and challenges associated with genetic knowledge in personalized nutrition. Ethical concerns, access and affordability issues, the complexity of gene-diet interactions, overemphasis on genetics, the risk of stigmatization and discrimination, and the potential for inaccurate interpretations all need to be carefully considered and managed in order to balance the benefits and risks of nutrigenomics.
Call for Moderation in Utilizing Genetic Knowledge
A key takeaway from this discussion is the importance of moderation in utilizing genetic knowledge in personalized nutrition. While genetics play a significant role in our health and dietary responses, they are just one piece of the puzzle. It is essential to consider other important health factors, such as lifestyle, environment, and socio-economic circumstances, to develop comprehensive and effective personalized nutrition plans. A balanced approach that takes into account all relevant factors will lead to more accurate and meaningful recommendations that truly optimize health outcomes.
Emphasizing the Need for Further Research and Education
As the field of nutrigenomics continues to evolve, further research and education are essential. Ongoing research is needed to advance our understanding of gene-diet interactions, improve research methodologies, and refine dietary recommendations based on the latest scientific evidence. Additionally, public education and awareness about nutrigenomics are crucial to ensure individuals have a clear understanding of the benefits, risks, and limitations of genetic knowledge in personalized nutrition. By fostering a well-informed public and healthcare professionals, we can work towards the responsible and sustainable integration of nutrigenomics into healthcare systems and dietary practices, ultimately optimizing individual health outcomes.



