Nutrigenomics, the study of how genes interact with nutrients, holds immense promise for personalized nutrition. As research continues to advance in this field, it uncovers fascinating insights into the connection between our genetic makeup and our dietary needs. The benefits of nutrigenomics lie in its ability to provide individuals with targeted, science-backed recommendations for optimal nutrition. By understanding an individual’s genetic variations related to nutrition, personalized nutrition plans can be tailored to their specific needs, leading to improved overall health and well-being. In this article, we will explore the exciting new research in nutrigenomics, the prevalence of genetic variants related to nutrition, the advantages of personalized nutrition, and practical ways to incorporate this knowledge into everyday life. If you’re interested in unlocking the potential of your genetic code to enhance your diet and health, read on to discover the benefits of nutrigenomics for personalized nutrition.
Understanding Nutrigenomics
Nutrigenomics is a field of study that explores the interaction between our genes and our diet, and how this interplay can influence our health and well-being. By understanding how our unique genetic makeup affects how we metabolize and respond to different nutrients, researchers and healthcare professionals can develop personalized nutrition plans that cater to individual needs and optimize health outcomes.
Definition and Basic Concepts of Nutrigenomics
Nutrigenomics, also known as nutritional genomics, is a branch of science that investigates how our genes affect our response to the foods we eat. It seeks to uncover the specific genetic variants that impact an individual’s nutritional needs, as well as how dietary factors can influence gene expression and overall health.
At its core, nutrigenomics aims to uncover the intricate relationships between our genetic makeup, the food we consume, and our health outcomes. By understanding these relationships, researchers can develop personalized nutrition strategies to help individuals prevent and manage chronic diseases, improve their overall well-being, and optimize their nutritional status.
The Interplay between Genes and Diet
Our genes play a crucial role in determining how our bodies metabolize and respond to the food we consume. Genetic variants, or small variations in our DNA sequence, can affect the way our bodies process nutrients, absorb vitamins and minerals, and metabolize macronutrients.
For example, certain genetic variants may influence an individual’s ability to digest lactose, the sugar found in milk and dairy products. People with lactose intolerance have lower levels of the enzyme lactase, which is responsible for breaking down lactose. By understanding these genetic variants, individuals can tailor their diets to reduce their intake of lactose-containing foods and improve their digestive health.
Furthermore, our diet can also influence the expression of our genes. Certain nutrients can turn genes on or off, affecting various biological processes in our bodies. This interplay between genes and diet highlights the importance of personalized nutrition, as it recognizes that individuals may respond differently to the same diet due to their unique genetic makeup.
The Role of Nutrigenomics in Health and Disease Prevention
Nutrigenomics has the potential to revolutionize healthcare and disease prevention by providing targeted and personalized nutrition advice. By understanding an individual’s genetic variants and how they interact with specific food components, healthcare professionals can create personalized nutrition plans that can help prevent, manage, or even reverse certain chronic diseases.
For instance, nutrigenomics research has identified genetic variants associated with an increased risk of developing cardiovascular disease. By accounting for these genetic factors, healthcare professionals can recommend specific dietary changes, such as reducing sodium intake or increasing omega-3 fatty acid consumption, to optimize cardiovascular health.
In addition, nutrigenomics can also help identify individuals who may have an increased risk of developing nutrition-related conditions, such as type 2 diabetes or obesity. By understanding an individual’s genetic predisposition, healthcare professionals can provide personalized dietary recommendations to mitigate these risks and promote optimal health.
Genetic Variants and Their Relation to Nutrition
Influence of Genetic Variants on Individual Nutritional Needs
Our genes influence various aspects of our nutritional needs, ranging from macronutrient metabolism to micronutrient requirements. Genetic variants can impact an individual’s ability to metabolize certain nutrients and may affect their absorption, utilization, or storage within the body.
For example, genetic variations in the FTO gene have been associated with increased appetite and a higher risk of obesity. Individuals with these genetic variants may have a reduced ability to regulate their food intake, making it more challenging for them to maintain a healthy weight. By understanding these genetic influences, personalized nutrition plans can be developed to address these specific needs and help individuals achieve their weight management goals.
Common Genetic Variants Affecting Food Metabolism
There are several well-known genetic variants that impact how our bodies metabolize and respond to specific nutrients. For instance, variations in the MTHFR gene can affect the body’s utilization of folate, a B-vitamin essential for many biochemical processes. This genetic variant can influence an individual’s susceptibility to certain health conditions, such as neural tube defects or cardiovascular disease, and may require specific dietary interventions to ensure adequate folate intake and metabolism.
Similarly, variations in the CYP1A2 gene can affect the rate at which caffeine is metabolized. Individuals with genetic variants associated with slow caffeine metabolism may be more sensitive to the effects of caffeine and may need to limit their intake to avoid side effects such as restlessness or sleep disturbances.
How Personal Genetics Affect Dietary Responses
By understanding an individual’s personal genetics, healthcare professionals can tailor dietary interventions to optimize their response to specific foods or nutrients. Personalized nutrition approaches take into account an individual’s genetic variations that may impact their dietary requirements, tolerances, or sensitivities.
For example, individuals with genetic variants associated with lower levels of certain digestive enzymes, such as amylase or lactase, may benefit from adjusting their diet accordingly. These individuals may need to consume a lower-carbohydrate diet or reduce their intake of lactose-containing foods to optimize digestion and minimize discomfort.
Furthermore, individuals with specific genetic variations may have different responses to certain dietary interventions. For example, some studies have shown that individuals with certain genotypes may respond better to low-carbohydrate diets for weight management, while others may benefit more from low-fat approaches. Understanding these genetic differences can help individuals and healthcare professionals identify the most effective dietary strategies for each individual.

This image is property of www.eurekaselect.com.
The Importance of Personalized Nutrition
Why One-Size-Fits-All Diets Do Not Always Work
One-size-fits-all diets or generic dietary guidelines are based on population averages and do not take into account individual genetic variations. While these guidelines may provide general recommendations for the population as a whole, they do not consider the unique genetic factors that influence how individuals metabolize and respond to food.
Individuals have different nutritional requirements and can respond differently to the same diet based on their genetic makeup. Nutrigenomics recognizes this individual variability and emphasizes the need for personalized nutrition approaches to optimize health outcomes.
Impact of Personalized Nutrition on Chronic Disease Management
Personalized nutrition can have a significant impact on chronic disease management. By understanding an individual’s genetic predisposition to certain conditions or their response to specific nutrients, healthcare professionals can develop targeted dietary interventions to mitigate risks and improve health outcomes.
For example, individuals with genetic variations associated with impaired glucose metabolism may benefit from personalized nutrition interventions that focus on carbohydrate management and glycemic control. By tailoring their carbohydrate intake to their specific genetic needs, individuals can better manage their blood sugar levels and reduce their risk of developing or worsening diabetes.
Enhancing Overall Well-being Through Personalized Nutrition
In addition to chronic disease management, personalized nutrition can enhance overall well-being and quality of life. By tailoring dietary recommendations to an individual’s genetic profile, personalized nutrition can help optimize nutrient intake, enhance energy levels, improve digestion, support mental health, and promote overall vitality.
For instance, individuals with genetic variations associated with decreased vitamin D synthesis may be more susceptible to deficiencies. By recognizing these genetic influences, personalized nutrition plans can encourage increased vitamin D intake through diet or supplementation to support bone health and maintain optimal immune function.
Advantages of Nutrigenomics-Based Personalized Nutrition
Better Understanding of Individual Dietary Needs
One of the key advantages of nutrigenomics-based personalized nutrition is the improved understanding of individual dietary needs. By analyzing an individual’s genetic makeup, healthcare professionals can gain valuable insights into their unique nutritional requirements, sensitivities, and tolerances.
This comprehensive understanding allows for the creation of targeted nutrition plans that can maximize nutrient intake, optimize metabolic processes, and minimize the risk of adverse reactions. It empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their diet and provides them with the tools they need to achieve their health and wellness goals.
Improved Weight Management Strategies
Weight management is a significant concern for many individuals, and personalized nutrition can play a crucial role in effective and sustainable weight loss or weight maintenance strategies. By taking into account an individual’s genetic variation and its impact on factors such as appetite regulation, metabolism, and fat storage, personalized nutrition plans can be tailored to address these specific needs.
For example, individuals with genetic variants associated with increased circulating levels of ghrelin, the hunger hormone, may benefit from personalized nutrition plans that focus on appetite control through specific dietary changes or meal timing strategies. By addressing these genetic factors, individuals can better manage their appetite, improve satiety, and enhance their weight management efforts.
Reducing Risks of Nutrition-Related Diseases
Nutrition-related diseases, such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer, are major health concerns. By identifying an individual’s genetic predisposition to these conditions, personalized nutrition can play a vital role in reducing their risks.
Personalized nutrition plans can be tailored to optimize nutrient intake, minimize the consumption of pro-inflammatory foods, and address specific genetic factors that may increase an individual’s susceptibility to these diseases. For example, individuals with genetic variations associated with impaired lipid metabolism may benefit from personalized nutrition plans that focus on reducing saturated fat intake and increasing the consumption of heart-healthy fats, such as omega-3 fatty acids.

This image is property of dietcarenutrition.com.
Real-Life Applications of Nutrigenomics
Case Studies of Nutrigenomics in Action
Nutrigenomics has already shown promising results in real-life applications, with numerous case studies demonstrating the benefits of personalized nutrition interventions. For example, a study conducted on individuals with a specific genetic variant in the FTO gene showed that those who followed a personalized diet based on their genetic profile lost more weight and experienced greater improvements in metabolic health compared to those on a standard weight loss program.
In another case study, individuals with a genetic variant associated with impaired caffeine metabolism were advised to reduce their caffeine intake to minimize the risk of adverse effects. By implementing this personalized nutrition recommendation, these individuals reported improved sleep quality, reduced jitters, and fewer digestive disturbances.
How Nutrigenomics Benefits Athletes
Athletes face unique nutritional challenges, as their bodies require optimal fueling, recovery, and performance support. Nutrigenomics can offer valuable insights into an athlete’s nutritional needs, genetic variations that may affect their response to specific nutrients, and strategies to enhance training adaptations and performance outcomes.
For example, personalized nutrition interventions based on an athlete’s genetic profile can help optimize macronutrient ratios, nutrient timing, and the intake of specific vitamins and minerals essential for athletic performance. By addressing individual genetic factors, personalized nutrition can help athletes reach their full potential and achieve their training and competition goals.
Nutrigenomics in Managing Food Allergies and Intolerances
Food allergies and intolerances can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life and overall health. Nutrigenomics has the potential to improve the management of these conditions by identifying genetic factors that may contribute to certain sensitivities or intolerances.
By understanding an individual’s genetic variations, healthcare professionals can tailor dietary recommendations to avoid specific allergens or intolerant foods while ensuring optimal nutrient intake. Personalized nutrition plans can help individuals navigate their dietary restrictions and find suitable alternatives to promote a well-balanced diet and minimize the risk of nutrient deficiencies.
Testing for Nutrigenomics: The Process and Benefits
The Process of Genetic Testing for Nutrigenomics
Genetic testing for nutrigenomics involves analyzing an individual’s DNA to identify specific genetic variants that may influence their nutritional needs, sensitivities, or tolerances. This involves collecting a DNA sample, typically through a saliva or blood sample, and processing it in a laboratory using advanced genetic analysis techniques.
Once the genetic data is obtained, it is compared against a database of known genetic variations that have been associated with specific nutrition-related traits or conditions. This analysis provides insights into an individual’s unique genetic profile and guides the development of personalized nutrition recommendations.
Safety and Effectiveness of Genetic Testing
Genetic testing for nutrigenomics is generally considered safe and non-invasive, as it typically involves collecting a saliva sample or a small blood sample. However, it is essential to ensure that genetic testing is conducted by reputable and certified laboratories to ensure accurate and reliable results.
While the field of nutrigenomics is continuously advancing, it is crucial to recognize that genetic testing is just one piece of the puzzle. Personalized nutrition recommendations should be based on a holistic approach that considers an individual’s genetic profile in conjunction with other factors such as medical history, lifestyle, and dietary preferences.
Interpreting and Applying Test Results
Interpreting the results of genetic testing for nutrigenomics requires expertise and a deep understanding of both genetics and nutrition. Trained healthcare professionals, such as registered dietitians or healthcare practitioners specializing in nutrigenomics, can interpret the test results and develop personalized nutrition recommendations tailored to an individual’s unique genetic makeup.
Applying test results involves translating the genetic information into actionable dietary advice, including specific nutrient targets, dietary modifications, and strategies to optimize health outcomes. By understanding how an individual’s genes interact with their diet, healthcare professionals can create practical and sustainable personalized nutrition plans to help individuals achieve their health and wellness goals.
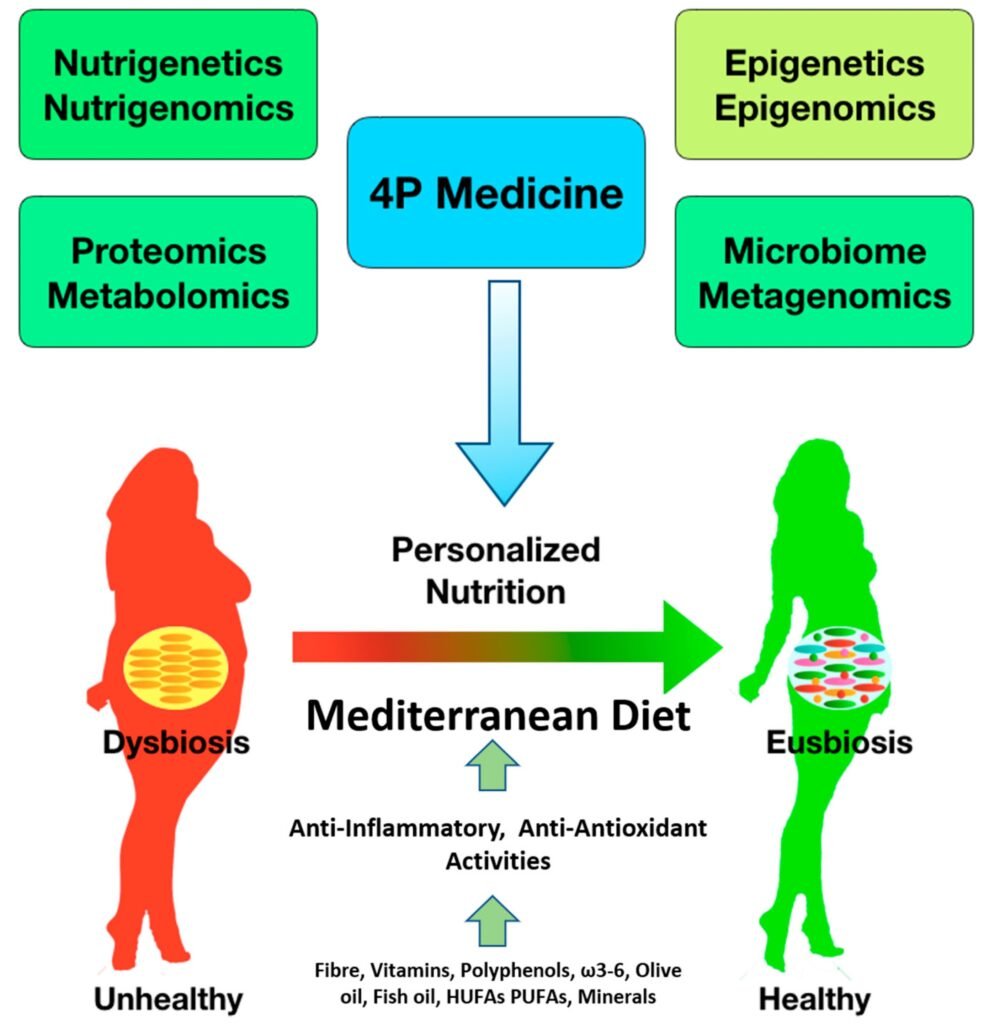
This image is property of www.mdpi.com.
Challenges and Controversies in Nutrigenomics
Debate over the Effectiveness of Nutrigenomics
While nutrigenomics shows promise as a tool for personalized nutrition, there is an ongoing debate over its effectiveness and practicality. Some critics argue that the field is still in its early stages and that the evidence supporting the benefits of personalized nutrition based on genetic testing is limited or inconclusive.
It is crucial to recognize that nutrigenomics is a rapidly evolving field, and advancements in technology and research continue to expand our understanding of how our genes interact with our diet. Long-term studies and large-scale clinical trials are needed to establish a robust evidence base for the efficacy and impact of nutrigenomics-based personalized nutrition interventions.
Potential Unintended Consequences of Genetic Testing
Genetic testing for nutrigenomics, like any other medical procedure, is not without its potential risks or unintended consequences. Some individuals may experience emotional distress or anxiety when confronted with information about their genetic variants or potential health risks.
Privacy concerns are also an important consideration when it comes to genetic testing. It is essential to ensure that genetic data is handled securely and confidentially to protect individuals’ privacy and prevent unauthorized use or access of genetic information.
Addressing Ethical Concerns in Nutrigenomics
As with any rapidly advancing scientific field, there are ethical concerns associated with nutrigenomics. For example, there is a debate surrounding genetic testing in children and the potential long-term implications of testing at an early age. It is essential to carefully consider the ethical implications of nutrigenomics and ensure that individuals’ autonomy, privacy, and well-being are respected.
To address these ethical concerns, guidelines and regulations are continually being developed to ensure the responsible and ethical use of genetic information in the context of personalized nutrition. These guidelines help healthcare professionals navigate the ethical considerations and provide individuals with the information and support they need to make informed decisions about genetic testing and personalized nutrition interventions.
The Future of Nutrigenomics
Emerging Research and Innovations in Nutrigenomics
The future of nutrigenomics is bright, with ongoing research and innovations continuing to deepen our understanding of the interplay between genes and nutrition. Advances in technology, such as next-generation sequencing and high-throughput gene expression analysis, are allowing researchers to gather more comprehensive and accurate genetic data.
Furthermore, the integration of multi-omics approaches, such as combining genetic data with transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics, is providing a more holistic understanding of how our genes interact with our diet at a molecular level. This integrative approach holds great potential for uncovering new insights and developing more precise personalized nutrition interventions.
The Potential Impact of AI and Machine Learning on Nutrigenomics
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are poised to play a significant role in the future of nutrigenomics. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data, including genetic information and dietary records, to generate personalized nutrition recommendations tailored to individuals’ unique genetic profiles and health goals.
By leveraging AI and machine learning algorithms, healthcare professionals can streamline the process of analyzing genetic data, interpreting test results, and translating them into actionable dietary advice. This technology has the potential to make personalized nutrition interventions more accessible and scalable, ultimately improving health outcomes on a broader scale.

This image is property of media.springernature.com.
Educating Yourself About Nutrigenomics
Trusted Sources of Information on Nutrigenomics
When seeking information about nutrigenomics, it is crucial to rely on trusted and reputable sources. Websites or publications from reputable research institutions, government health organizations, and professional associations in the field of nutrition and genetics can provide reliable and evidence-based information.
Additionally, consulting with healthcare professionals who specialize in nutrigenomics, such as registered dietitians or genetic counselors, can offer personalized guidance and insights tailored to individual needs and goals. These professionals have the knowledge and expertise to interpret genetic test results, develop personalized nutrition plans, and answer any questions individuals may have about nutrigenomics.
Consulting Professionals for Personalized Nutrition Advice
While there is a wealth of information available on nutrigenomics, consulting with healthcare professionals is essential to receive personalized nutrition advice based on an individual’s genetic profile. Registered dietitians, healthcare practitioners specializing in nutrigenomics, or genetic counselors have the expertise to interpret genetic test results, consider other relevant factors, and develop tailored nutrition recommendations.
When seeking personalized nutrition advice, it is important to choose a healthcare professional who has experience and credentials in the field of nutrigenomics. They can provide individuals with the guidance and support needed to implement personalized nutrition strategies and optimize health outcomes.
Conclusion: Embracing Nutrigenomics for Your Health
Embracing nutrigenomics and personalized nutrition has the potential to revolutionize the way we approach our health and well-being. By recognizing the interplay between our unique genetic makeup and our dietary choices, we can optimize our nutritional status, prevent chronic diseases, and enhance our overall well-being.
Through genetic testing and the expertise of healthcare professionals specializing in nutrigenomics, individuals can gain valuable insights into their genetic variations and how these influence their nutritional needs, sensitivities, or tolerances. Armed with this knowledge, individuals can make informed dietary decisions, implement personalized nutrition strategies, and take proactive steps towards their health and wellness goals.
In conclusion, nutrigenomics offers exciting possibilities for personalized nutrition, harnessing the power of our genes to optimize our health. By embracing this field and seeking guidance from qualified professionals, individuals can unlock the potential of personalized nutrition and embark on a journey towards optimal health and well-being.
Summary of the Key Benefits of Nutrigenomic-Based Personalized Nutrition
- Nutrigenomics recognizes the interplay between genes and diet, allowing for personalized nutrition plans tailored to an individual’s genetic makeup.
- Personalized nutrition can improve chronic disease management and reduce the risk of nutrition-related conditions.
- By understanding an individual’s genetic variations, healthcare professionals can optimize dietary strategies for weight management.
- Nutrigenomics can enhance overall well-being by addressing individual nutritional needs and optimizing nutrient intake.
- Real-life case studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of personalized nutrition interventions based on nutrigenomics.
- Athletes can benefit from personalized nutrition plans tailored to their genetic profile to optimize performance and recovery.
- Nutrigenomics can help manage food allergies and intolerances by identifying genetic factors that may contribute to these conditions.
- Genetic testing for nutrigenomics is a safe and effective process, but it should be conducted by reputable laboratories.
- Addressing ethical concerns and privacy issues is crucial in the field of nutrigenomics.
- The future of nutrigenomics holds promise with ongoing research and innovative technologies, such as AI and machine learning.
- Trusted sources of information and consulting professionals specializing in nutrigenomics are essential for accurate and personalized advice.
- Individuals can take the first step towards implementing nutrigenomics in their lives by learning more about genetic testing options and personalized nutrition strategies.

This image is property of d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net.
Taking the First Step to Implement Nutrigenomics in Your Life
If you’re interested in exploring the possibilities of personalized nutrition based on nutrigenomics, there are several steps you can take to get started.
Educate yourself: Seek reliable sources of information on nutrigenomics, such as reputable research institutions, government health organizations, and professional associations. Stay up to date with the latest research and developments in the field to make informed decisions.
Consult a healthcare professional: Reach out to registered dietitians, healthcare practitioners specializing in nutrigenomics, or genetic counselors. These professionals can provide personalized guidance, interpret genetic test results, and develop tailored nutrition recommendations based on your genetic profile.
Consider genetic testing: If you’re curious about your unique genetic makeup and how it may influence your nutritional needs, consider genetic testing. Choose a reputable laboratory that specializes in nutrigenomics and offers comprehensive analysis of genetic variants related to nutrition.
Interpretation and application of test results: After receiving your genetic test results, consult with a healthcare professional to interpret the findings and translate them into practical dietary strategies. They can help you create a personalized nutrition plan that takes into account your genetic variations and supports your health goals.
Implement personalized nutrition strategies: Incorporate the personalized nutrition recommendations into your daily life. This may involve modifying your diet to meet specific nutrient targets, adjusting macronutrient ratios, avoiding certain allergenic foods, or integrating personalized meal plans. Monitor your progress, assess how your body responds to the changes, and make adjustments as needed.
By embracing the field of nutrigenomics and working with healthcare professionals, you can take the first step towards implementing personalized nutrition strategies that optimize your health and well-being. Remember, personalized nutrition is a journey, and it requires ongoing commitment and collaboration to achieve sustainable results.



