Genetic testing in personalized nutrition offers numerous benefits that can revolutionize the way we approach health and wellness. Firstly, it enables the customization of dietary plans based on individual genetic profiles, optimizing health outcomes, and reducing the risk of disease. By understanding how our genes interact with specific nutrients, we can tailor our diets to address potential deficiencies or sensitivities and promote overall well-being. Secondly, genetic testing in personalized nutrition can inform targeted dietary interventions for disease prevention and management. By identifying genetic markers associated with conditions like obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases, individuals can make proactive choices to mitigate their risk and improve their health. Lastly, genetic testing can enhance athletic performance and recovery by tailoring nutritional strategies to an individual’s genetic predispositions. By understanding how our genes influence factors such as metabolism and muscle response to nutrients, athletes can optimize their training and fueling strategies, enabling them to achieve peak performance. Through the benefits of genetic testing in personalized nutrition, we can unlock the power of our genes to improve our health and well-being.

This image is property of www.mdpi.com.
Understanding Nutrigenomics
Nutrigenomics is a field of study that focuses on understanding how genetics influence an individual’s response to diet. By exploring the intricate relationship between genes and nutrition, we can gain valuable insights into personalized nutrition strategies that can optimize health outcomes.
Gene-diet interactions are a key aspect of nutrigenomics. These interactions occur when specific genes influence how the body processes and responds to nutrients. This means that an individual’s genetic makeup can affect their metabolism, nutrient absorption, and overall dietary requirements.
Two important concepts in nutrigenomics are gene expression and epigenetics. Gene expression refers to the process by which information from genes is used to create functional products, such as proteins, in the body. Epigenetics, on the other hand, explores how gene expression can be influenced by external factors, including diet and lifestyle choices. Understanding gene expression and epigenetics allows us to tailor dietary plans to an individual’s specific genetic profile.
Applications of Nutrigenomics
The applications of nutrigenomics are wide-ranging and have profound implications for health and wellness. By customizing dietary plans based on an individual’s genetic profile, we can optimize health outcomes and prevent disease.
In terms of health implications, nutrigenomics enables the customization of dietary plans to promote overall well-being and prevent chronic conditions. By understanding an individual’s genetic variations, we can tailor their diet to support optimal health and reduce the risk of conditions such as obesity, heart disease, and diabetes.
Nutrigenomics also plays a crucial role in disease prevention and management. By identifying genetic variations that predispose individuals to specific conditions, we can design targeted dietary interventions to reduce the risk and progression of these diseases. For example, individuals with a genetic predisposition to diabetes may benefit from personalized dietary plans that focus on blood sugar regulation and insulin sensitivity.
Sports performance can also be enhanced through gene-informed nutrition strategies. By understanding an individual’s genetic predispositions, such as their ability to metabolize certain nutrients or their susceptibility to inflammation, we can develop personalized nutrition plans that optimize athletic performance, enhance recovery, and reduce the risk of injuries.
This image is property of pub.mdpi-res.com.
Challenges and Limitations
While nutrigenomics holds great promise, there are several challenges and limitations that need to be addressed. One of the main ethical considerations is related to the use of genetic information in personalized nutrition. Privacy concerns and the potential for genetic discrimination need to be carefully addressed to ensure the responsible use and protection of individuals’ genetic data.
Access and affordability are also significant challenges. Nutrigenomic testing and personalized nutrition services may not be accessible to all individuals due to financial constraints or limited availability. Efforts should be made to make these services more widely accessible to diverse populations.
The complexity of gene-diet interactions is another challenge. The interplay between genes and dietary factors is multifaceted and not yet fully understood. Current research methodologies have limitations, and further exploration is needed to unravel the complexities involved in these interactions.
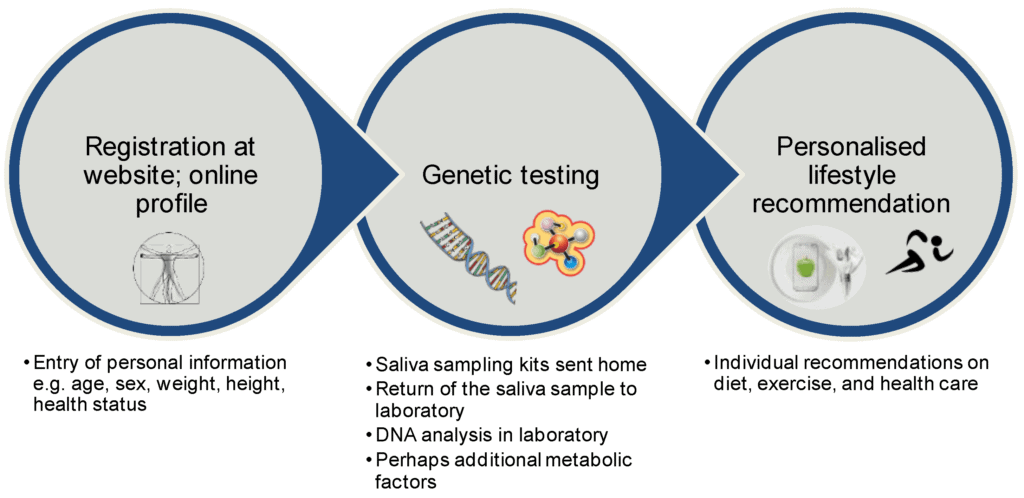
DNA-based Dietary Recommendations
Genetic testing plays a crucial role in the formulation of personalized diets. By analyzing an individual’s genetic information, we can identify specific variations that impact their response to certain dietary components. This information allows us to customize dietary recommendations to better suit an individual’s genetic profile and optimize their health outcomes.
Individual genetic variations can significantly influence an individual’s dietary requirements. For example, some individuals may have genetic variations that affect their ability to metabolize certain nutrients, such as vitamins or minerals. By understanding these variations, we can tailor their diet to prevent nutritional deficiencies and ensure optimal nutrient absorption.
Nutrigenomic data can also help identify individuals who may be at a higher risk of specific nutrient deficiencies. By assessing an individual’s genetic profile, we can determine their susceptibility to deficiencies in key nutrients and develop targeted strategies to prevent these deficiencies from occurring.
This image is property of media.springernature.com.
Advantages of Personalized Nutrition
Personalized nutrition offers numerous benefits for individuals looking to optimize their health and well-being. One notable advantage is its potential for weight management. By understanding an individual’s genetic variations related to metabolism, appetite regulation, and fat storage, customized dietary plans can be developed to support healthy weight loss or maintenance.
Furthermore, personalized nutrition can play a crucial role in disease prevention. By tailoring dietary plans to an individual’s genetic profile, we can target specific risk factors and reduce the likelihood of developing certain conditions. For example, individuals with a genetic predisposition to heart disease can benefit from personalized diets that focus on cardiovascular health and reduce the risk of developing heart-related complications.
Additionally, personalized nutrition can enhance sports performance and recovery. By considering an individual’s genetic variations related to nutrient metabolism, inflammation, and muscle recovery, tailored nutrition plans can optimize athletic performance, promote faster recovery, and reduce the risk of injuries.
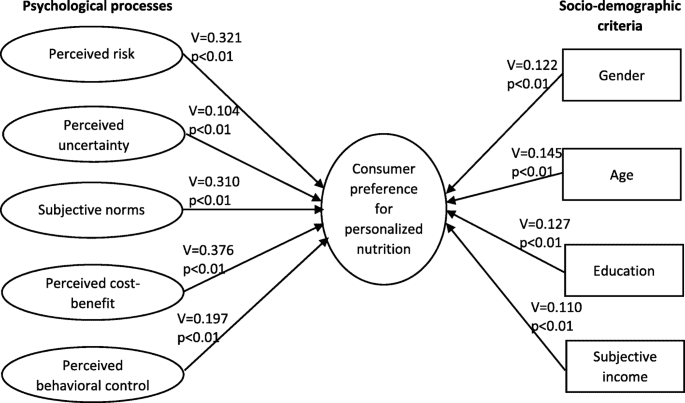
Controversies and Critiques of Nutrigenomics
While nutrigenomics offers exciting possibilities, it is not without its controversies and critiques. One major debate revolves around the efficacy of gene-based diets. While personalized nutrition has shown promising results, some argue that genetic variations alone may not provide sufficient information to develop effective dietary plans. Other factors, such as lifestyle, environmental factors, and cultural preferences, also play a crucial role in determining optimal nutrition.
Another criticism is the potential risk of over-reliance on genetic testing. Some experts worry that individuals may become overly dependent on genetic information and neglect other important aspects of nutrition and lifestyle choices. It is essential to strike a balance between genetic information and broader health guidelines to ensure comprehensive and holistic dietary recommendations.
There are also concerns about the potential for genetic discrimination. As nutrigenomics becomes more widely adopted, it is crucial to establish ethical guidelines and policies to protect individuals from potential discrimination based on their genetic data. To build public trust and confidence, there must be clear regulations and safeguards in place.

This image is property of www.frontiersin.org.
Ethical and Social Aspects
The integration of genetic information into personalized nutrition raises important ethical and social considerations. One significant concern is privacy. As genetic testing becomes more common, it is essential to protect individuals’ genetic information and ensure that it is used responsibly and securely.
Moreover, there is a potential for social disparities in access to nutrigenomic testing and personalized nutrition services. Financial constraints and limited availability could create inequalities and prevent certain groups from benefiting from these advancements. Efforts should be made to address these disparities and ensure equal access for all individuals.
To mitigate potential risks and promote responsible use, ethical guidelines and policies need to be established. These guidelines should address issues such as informed consent, data security, and the responsible use of genetic information. By providing clear guidelines, we can safeguard individuals and build trust in the field of nutrigenomics.
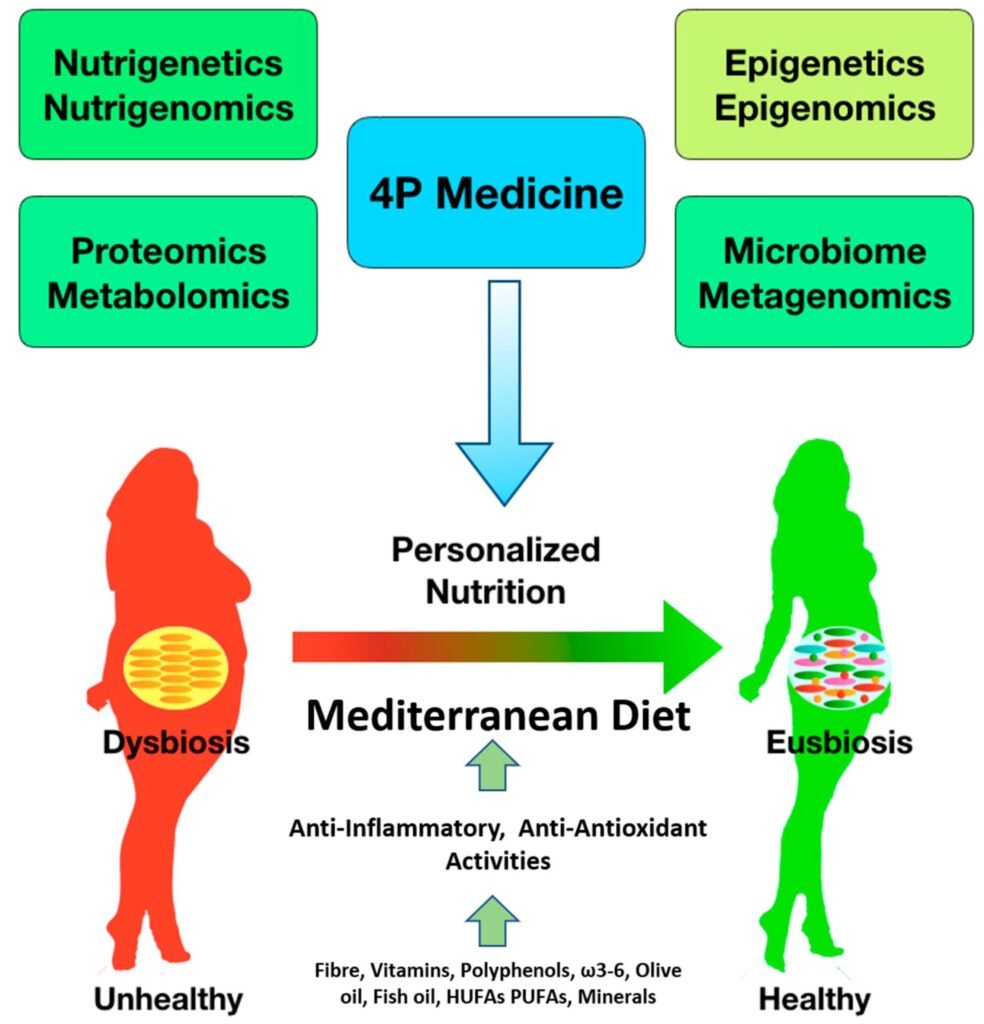
Commercial Aspects of Nutrigenomics
The commercialization of nutrigenomics has led to the marketing of genetic testing services for diet recommendations. Various companies offer personalized genetic testing kits that claim to provide insights into optimal nutrition based on individual genetic profiles. These services often involve the analysis of genetic variations related to metabolism, nutrient absorption, and dietary sensitivities.
Consumer perception and acceptance play a vital role in the success of these services. While some individuals may be eager to explore personalized nutrition options, others may have reservations or concerns about the reliability and utility of genetic testing. Clear and accurate communication, as well as education about the benefits and limitations of nutrigenomics, are crucial to building consumer trust and acceptance.
From an economic standpoint, the nutrigenomics market holds significant potential for growth. As more research is conducted and technologies advance, the demand for personalized nutrition services is expected to increase. This growth not only benefits individuals seeking personalized dietary plans but also creates opportunities for companies specializing in genetic testing and personalized nutrition services.
This image is property of www.mdpi.com.
Future Directions and Opportunities
The field of nutrigenomics is rapidly evolving, and significant advancements are expected in the coming years. Technological developments, such as advanced sequencing techniques and artificial intelligence, hold great promise for expanding our understanding of gene-diet interactions and enhancing personalized nutrition strategies.
Furthermore, the integration of nutrigenomics into mainstream healthcare practices represents a significant opportunity. By incorporating genetic information into preventive medicine and wellness programs, healthcare providers can offer personalized dietary plans and interventions that promote individual health and well-being.
Public education and awareness are crucial in shaping the future of nutrigenomics. By educating the public about the potential impact of genetics on nutrition and health, we can foster informed decision-making and empower individuals to make choices that optimize their well-being. Additionally, increasing public awareness can drive demand for further research and funding in the field.
Conclusion: The Future of Nutrigenomics
In conclusion, nutrigenomics offers an exciting frontier for personalized nutrition and health optimization. By understanding the intricate relationship between genetics and nutrition, we can tailor dietary plans based on individual genetic profiles to optimize health outcomes and prevent disease.
However, there are challenges and limitations that need to be addressed, such as ethical considerations, access and affordability issues, and the complexity of gene-diet interactions. With careful regulation, increased accessibility, and further research, nutrigenomics can provide valuable insights into personalized nutrition and revolutionize healthcare practices.
To fully realize the potential of nutrigenomics, there is a need for continued research, education, and integration into healthcare systems and dietary practices. By working together, researchers, healthcare professionals, policymakers, and individuals can collectively shape the future of nutrigenomics and unlock its full potential for individual well-being and public health.
Related Posts: Interaction between genetic susceptibility to obesity and food intake on BMI in Finnish school-aged children, The Impact of Malnutrition on Epigenetics: Exploring the Relationship between Genetics and Nutrition, Understanding the Impact of Genetics on Health Through Nutrigenomics, How does epigenetics impact personalized nutrition strategies?, Benefits of Genome Sequencing in Nutrigenomics



