In the fascinating world of nutrition and genomics, there is an intricate relationship waiting to be explored. This article delves into the field of nutrigenomics, which examines how our genetic makeup influences our individual responses to diet. By understanding this connection, personalized nutrition plans can be developed to optimize health outcomes. From understanding gene-diet interactions to exploring the applications and challenges of nutrigenomics, this article takes you on a journey through the fascinating world where genetics and nutrition intersect. By the end, you’ll be inspired to continue the research, education, and integration of nutrigenomics into healthcare systems and dietary practices to optimize individual health outcomes.
Understanding Nutrigenomics
Nutrigenomics, a relatively new field of study, focuses on understanding how genetic variations impact dietary responses. It explores the intricate relationship between nutrition and genomics to uncover how individualized dietary plans can optimize health outcomes based on individual genetic profiles.
Definition and Scope of Nutrigenomics
Nutrigenomics can be defined as the study of how an individual’s genetic makeup influences their body’s response to nutrients and how this interaction affects overall health. The scope of nutrigenomics is wide, encompassing research in genetics, nutrition, and biochemistry. It involves examining specific genes and their impact on metabolism, nutrient absorption, and other physiological functions.
Explanation of Gene-Diet Interactions
Gene-diet interactions refer to the ways in which specific genes influence how the body processes and responds to nutrients from the diet. Genetic variations can affect an individual’s ability to metabolize certain nutrients or predispose them to certain nutrient deficiencies or intolerances. Understanding these interactions is crucial in developing personalized nutritional strategies that can optimize health outcomes.
Introduction to Key Concepts: Gene Expression and Epigenetics
Gene expression refers to the process by which the information encoded in genes is used to create proteins and other molecules necessary for bodily functions. Nutrigenomics examines how dietary factors can influence the expression of certain genes and impact overall health.
Epigenetics, on the other hand, is the study of changes in gene expression that do not involve alterations in the DNA sequence itself. It explores how environmental factors, including diet, can modify gene activity. Nutrigenomics considers epigenetics as a crucial factor in understanding how nutrition influences gene-diet interactions and subsequently affects health outcomes.
Applications of Nutrigenomics
Understanding the applications of nutrigenomics is essential in comprehending its potential impact on personalized nutrition and overall health outcomes.
Health Implications of Nutrigenomics
Nutrigenomics has significant health implications as it allows for the customization of dietary plans based on an individual’s genetic profile. By analyzing an individual’s genetic variations, nutrigenomics can identify specific nutrients that may promote health or increase the risk of certain diseases. This knowledge enables healthcare professionals to tailor dietary recommendations to optimize an individual’s overall health and well-being.
Disease Prevention and Management
Nutrigenomics can inform targeted dietary interventions for preventing and managing various health conditions. By understanding an individual’s genetic predispositions to certain diseases, such as obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases, personalized dietary plans can be developed to mitigate risk factors and improve health outcomes. This approach to disease prevention and management holds great potential in improving public health and reducing the burden of chronic diseases.
Performance Enhancement through Nutrigenomics
Athletic performance and recovery can be enhanced through an understanding of nutrigenomics. By tailoring nutritional strategies to an athlete’s genetic predispositions, nutrigenomics can optimize nutrient utilization, improve energy metabolism, and support muscle recovery. This personalized approach to nutrition can help athletes achieve their peak performance and reduce the risk of injuries.
This image is property of cdn-wordpress-info.futurelearn.com.
Challenges and Limitations of Nutrigenomics
While nutrigenomics holds immense potential, it also faces several challenges and limitations that need to be addressed.
Ethical Considerations
One of the key ethical considerations in nutrigenomics is the responsible and ethical use of genetic information. There are concerns about privacy, informed consent, and the potential misuse of genetic data. Safeguarding individuals’ genetic information and ensuring that it is used in a responsible and transparent manner is crucial for the ethical practice of nutrigenomics.
Access and Affordability
Another challenge is ensuring equitable access to nutrigenomic testing and personalized nutrition services. Currently, these services are often expensive and not easily accessible to all populations. Addressing the affordability and availability of nutrigenomic testing and personalized nutrition services is essential to ensure that the potential benefits of nutrigenomics are accessible to all individuals, regardless of their socioeconomic status.
Complexity of Gene-Diet Interactions
Understanding the complexities involved in gene-diet interactions is another challenge in nutrigenomics. Genetic variations do not work in isolation, and their interactions with dietary factors are complex and multifaceted. Deciphering these intricacies requires further research and advancements in methodologies. Furthermore, individual responses to dietary interventions can vary greatly, making it difficult to draw definitive conclusions. More research is needed to enhance our understanding of gene-diet interactions and their implications for personalized nutrition.
Future Directions and Opportunities in Nutrigenomics
The future of nutrigenomics is full of possibilities, driven by advancements in technology and a growing awareness of the potential benefits it holds.
Advancements in Technology
Advancements in technology, such as advanced sequencing techniques and high-throughput data analysis, are revolutionizing the field of nutrigenomics. These technologies allow for a more comprehensive and detailed analysis of an individual’s genetic profile, enabling a deeper understanding of gene-diet interactions. Furthermore, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms has the potential to accelerate the discovery of gene-nutrient associations and improve personalized nutrition recommendations.
Integration of Nutrigenomics into Mainstream Healthcare
The integration of nutrigenomics into mainstream healthcare practices is a promising direction for the field. By incorporating genetic information into routine medical assessments, healthcare professionals can develop personalized treatment plans that consider an individual’s genetic predispositions and dietary needs. This integration has the potential to revolutionize preventive medicine, as well as the management of chronic diseases.
Public Education and Awareness About Nutrigenomics
Public education and awareness about nutrigenomics are crucial for its widespread adoption and acceptance. A well-informed public can make informed choices regarding their dietary habits and actively participate in their own health journey. Educating individuals about the benefits and implications of personalized nutrition can empower them to make healthier choices and optimize their overall well-being.

This image is property of foodnwellness.com.
Impact of Genetics on Nutrient Absorption and Metabolism
An individual’s genetics can significantly influence their nutrient absorption and metabolism, highlighting the importance of understanding the genetic basis of these processes.
How Genetics Affect Nutrient Absorption
Genetic variations can impact the body’s ability to absorb and utilize certain nutrients. For example, variations in genes involved in the breakdown and absorption of lactose can lead to lactose intolerance. Similarly, genetic variations in the genes responsible for vitamin D metabolism can affect an individual’s ability to metabolize and utilize vitamin D. By understanding these genetic variations, personalized dietary recommendations can be made to accommodate individual nutrient absorption needs.
Role of Genetics in Metabolism
Genetics plays a vital role in metabolism, influencing how the body processes and utilizes nutrients for energy production and other biochemical processes. Genetic variations in genes involved in metabolism can impact an individual’s metabolic rate, nutrient utilization, and energy expenditure. This understanding can guide personalized nutrition recommendations to optimize metabolic health and prevent metabolic disorders such as obesity and diabetes.
Difference in Nutrient Requirements Based on Genetics
Genetic variations can also influence an individual’s nutrient requirements. For example, some individuals may have genetic variations that affect their need for certain vitamins, such as folate or vitamin B12. Understanding these differences in nutrient requirements based on genetics can guide personalized dietary recommendations to ensure optimal nutrient intake and prevent nutrient deficiencies.
Genetic Variations and Food Intolerances
The genetic basis of food intolerances sheds light on how genetic variations can impact an individual’s responses to different foods.
Understanding the Genetic Basis of Food Intolerances
Genetic variations can influence an individual’s susceptibility to food intolerances. For example, lactose intolerance is often caused by a deficiency of the enzyme lactase, which breaks down lactose in the body. Genetic variations in the gene that encodes lactase can lead to reduced enzyme activity and result in lactose intolerance. Similarly, genetic variations can influence an individual’s response to gluten, causing conditions such as celiac disease.
Impact of Genetic Variations on Responses to Different Foods
Genetic variations can also impact an individual’s responses to different foods and dietary components. For example, some individuals may have variations in genes involved in the perception of taste or the metabolism of certain compounds, leading to differences in food preferences or sensitivities. Understanding these genetic variations can help individuals make informed choices about their dietary preferences and restrictions.
Case Studies of Food Intolerances Caused by Genetic Variations
Several case studies highlight the role of genetic variations in food intolerances. For example, a study found that individuals with a specific genetic variation in the FTO gene were more susceptible to experiencing an increased desire for high-calorie foods and had a higher risk of obesity. Another study identified genetic variations that influence an individual’s risk of developing lactose intolerance. These case studies showcase how genetic variations can contribute to food intolerances and inform personalized dietary recommendations.

This image is property of www.mdpi.com.
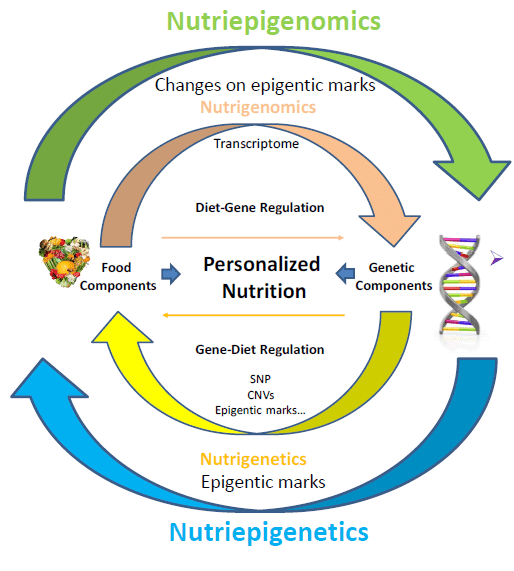
Gene-Diet Interactions and Personalized Nutrition
Understanding gene-diet interactions is essential for developing personalized nutrition plans that align with an individual’s genetic makeup and dietary needs.
Unpacking the Concept of Personalized Nutrition
Personalized nutrition aims to develop dietary plans tailored to an individual’s genetic profile, health goals, and dietary preferences. It considers an individual’s unique genetic variations, metabolic traits, nutrient requirements, and food sensitivities to create a personalized dietary approach. By taking into account an individual’s genetic predispositions, personalized nutrition can optimize nutrient intake, enhance metabolic health, and improve overall well-being.
The Role of Gene-Diet Interactions in Creating an Individualized Diet Plan
Gene-diet interactions play a crucial role in creating individualized diet plans. By analyzing an individual’s genetic profile and understanding how specific genes influence nutrient metabolism, absorption, and utilization, personalized nutrition can optimize nutrient intake and minimize the risk of nutrient deficiencies or intolerances. For example, individuals with genetic variations impacting vitamin D metabolism might require higher vitamin D intake to maintain optimal levels. By considering these genetic variations, personalized nutrition can tailor dietary recommendations to meet individual nutrient needs.
Benefits and Potential Drawbacks of Personalized Nutrition
Personalized nutrition offers several benefits, including improved health outcomes, optimized nutrient utilization, and enhanced dietary adherence. By aligning dietary recommendations with an individual’s genetic predispositions, personalized nutrition can increase the effectiveness of dietary interventions and reduce the risk of adverse effects.
However, there are also potential drawbacks to personalized nutrition. It requires access to genetic testing, which may not be universally available or affordable. Additionally, the interpretation of genetic data and its application to dietary recommendations is complex and requires the expertise of healthcare professionals. Ensuring the accuracy and validity of genetic testing results and the appropriate translation of genetic information into practical dietary advice are essential aspects of personalized nutrition.
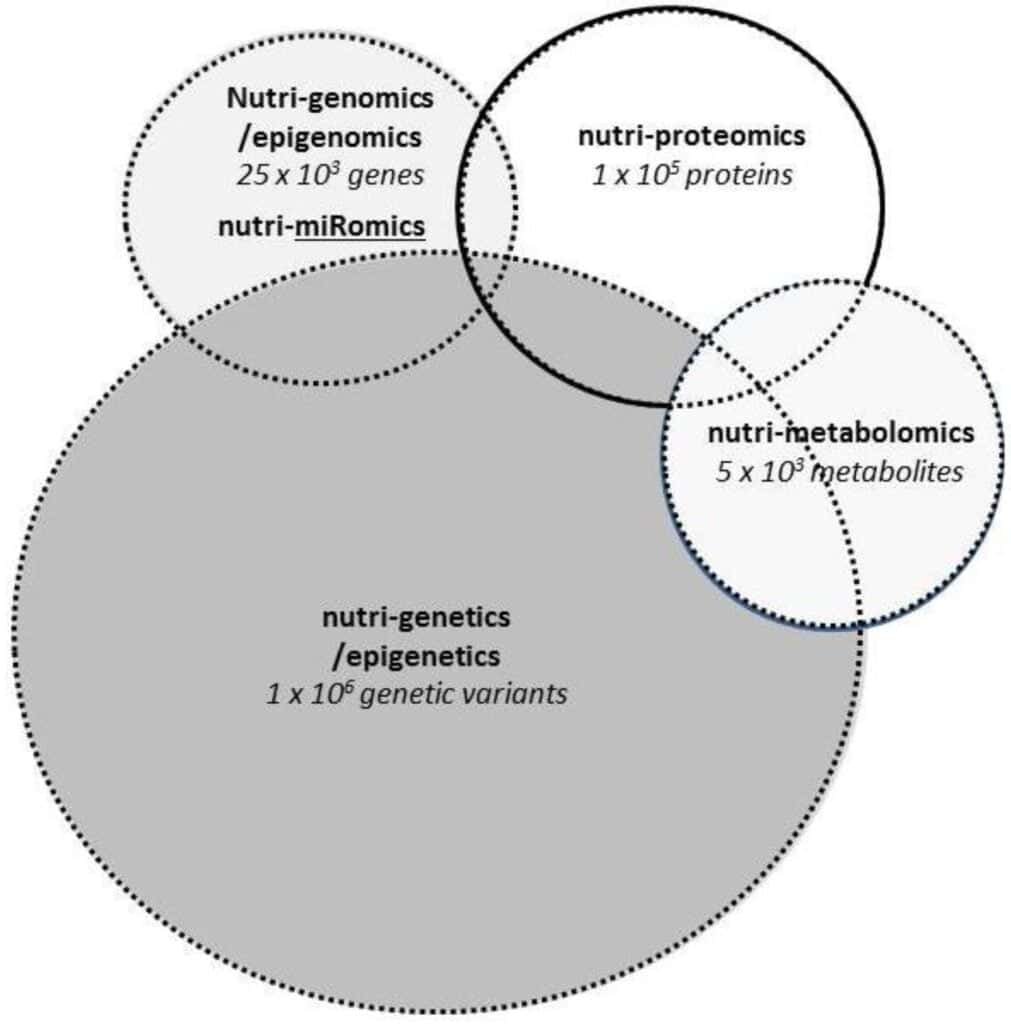
Genetic Testing for Personalized Nutrition
Genetic testing plays a crucial role in unraveling an individual’s genetic predispositions and guiding personalized nutrition recommendations.
Understanding the Process of Genetic Testing
Genetic testing involves analyzing an individual’s DNA to identify specific variations in genes associated with nutrient metabolism, absorption, and other factors relevant to personalized nutrition. It typically requires a sample of DNA, which can be obtained through saliva or a simple blood test. The DNA sample is then analyzed using advanced sequencing techniques to identify genetic variations.
Interpreting and Applying Genetic Testing Results for Personalized Nutrition
Interpreting and applying genetic testing results for personalized nutrition require expertise in genetics and nutrition. Healthcare professionals, such as registered dieticians or genetic counselors, can assess an individual’s genetic variations and align them with existing scientific evidence and dietary guidelines to develop personalized nutrition plans. Genetic testing results, when combined with thorough assessments of an individual’s overall health, dietary preferences, and goals, can provide valuable insights for optimizing nutrition.
Legalities and Privacy Concerns Surrounding Genetic Testing
Legal and privacy concerns surround the use of genetic testing for personalized nutrition. It is essential to ensure that individuals’ genetic information is protected and used responsibly. Laws and regulations regarding the use and storage of genetic information vary between countries. Safeguarding individuals’ privacy and obtaining informed consent are vital aspects of ethical genetic testing practices.
This image is property of pub.mdpi-res.com.
Case Studies in Nutrigenomics
Examining real-life cases applying nutrigenomics provides valuable insights into its practical applications, success stories, and challenges encountered.
Exploration of Real-Life Cases Applying Nutrigenomics
Real-life cases applying nutrigenomics involve assessing individuals’ genetic profiles and developing personalized nutrition plans based on their genetic variations. These cases can address various health conditions, performance optimization, or food intolerances, among others. By examining these cases, researchers and healthcare professionals can identify patterns, refine dietary recommendations, and assess the effectiveness of personalized nutrition interventions.
Success Stories and Challenges Encountered
Success stories in nutrigenomics underline the potential of personalized nutrition in improving health outcomes. For example, a case study might highlight how a personalized nutrition plan based on an individual’s genetic variations helped reduce the risk of obesity or improved metabolic health markers.
However, challenges are also encountered in implementing nutrigenomics in real-life cases. These challenges may include limited access to genetic testing, the complexity of interpreting genetic data, and the need for multidisciplinary collaboration among healthcare professionals to provide comprehensive care.
Interviews with Professionals and Patients Involved in Nutrigenomics
Interviews with professionals and patients involved in nutrigenomics can offer valuable insights into their experiences, perspectives, and outcomes. Professionals can share their expertise in applying nutrigenomics and the challenges they face, while patients can provide firsthand accounts of the impact of personalized nutrition on their health and well-being. These interviews can provide a holistic view of nutrigenomics, its practical applications, and its potential for improving public health.
Conclusion: The Future of Nutrition and Genomics
In conclusion, nutrigenomics offers a promising avenue for unraveling the intricate relationship between nutrition and genetics. By understanding gene-diet interactions and leveraging personalized nutrition, we can optimize health outcomes and prevent chronic diseases effectively. However, the field of nutrigenomics faces challenges, including ethical considerations, access and affordability, and the complexity of gene-diet interactions. Nonetheless, the future of nutrition and genomics holds immense potential, driven by advancements in technology, integration with healthcare, and public education and awareness. In order to maximize the potential impact of nutrigenomics on public health, continued research, education, and integration of this field into healthcare systems and dietary practices are essential. By embracing the opportunities presented by nutrigenomics, we can pave the way for a future where personalized nutrition is a cornerstone of optimal health and well-being.
Related Posts: Understanding the Role of Genomics in Nutrition, What is Nutrigenomics: Exploring the Relationship Between Genetics and Nutrition, Understanding the Impact of Genetic Variations on Dietary Responses, Epigenetic therapy and its role in personalized nutrition, The Application of Nutrigenomics in Personalized Nutrition



