In “The Future of Genomics: Exploring the Potential of Nutrigenomics,” you will delve into the intricate relationship between genetics and nutrition. This article aims to shed light on nutrigenomics, a field that explores how genetics influence individual responses to diet. By understanding gene-diet interactions, personalized nutrition strategies can be developed to optimize health outcomes. From disease prevention and management to performance enhancement, you will discover the diverse applications of nutrigenomics. However, this exciting field is not without its challenges, such as ethical considerations and accessibility. Looking ahead, advancements in technology and integration with healthcare hold promising opportunities. By the end of this article, you will not only understand the importance of nutrigenomics but also be compelled to contribute to its continued research, education, and integration into healthcare systems to optimize individual health outcomes.
This image is property of nap.nationalacademies.org.
Understanding Nutrigenomics
Nutrigenomics is a burgeoning field that focuses on understanding how genes interact with diet to influence individual responses. It encompasses the study of how genetic variations impact an individual’s dietary needs and responses, ultimately aiming to tailor personalized nutrition strategies to optimize health outcomes. Through nutrigenomics, scientists aim to uncover the intricate relationship between genetics and nutrition, shedding light on how our unique genetic makeup influences our dietary requirements.
In gene-diet interactions, specific genes are known to play a vital role in determining how our bodies process and respond to various nutrients. These gene variants, also known as alleles, can affect enzyme activity, nutrient absorption, and metabolism. By understanding these gene-diet interactions, scientists can develop targeted dietary plans that address the specific needs of individuals based on their genetic profiles.
An important aspect of nutrigenomics is the study of gene expression and epigenetics. Gene expression refers to the process through which genetic information is converted into functional proteins, which carry out various biological functions in the body. Epigenetics, on the other hand, refers to modifications in gene expression caused by factors other than changes in the DNA sequence itself. These epigenetic modifications can be influenced by environmental factors, including diet. Understanding how gene expression and epigenetics interact with nutrition can provide valuable insights into personalized nutrition strategies.
Applications of Nutrigenomics
The field of nutrigenomics offers a myriad of potential applications that can greatly benefit individuals in optimizing their health outcomes. One of the key applications is the customization of dietary plans based on an individual’s genetic profile. By analyzing an individual’s genetic makeup, nutritionists and healthcare professionals can tailor dietary recommendations to meet their specific nutritional needs, taking into account how their genes may influence their dietary responses. This level of personalization can help individuals achieve their health goals more effectively.
Additionally, nutrigenomics has significant implications for disease prevention and management. By understanding how an individual’s genetic variations interact with their diet, healthcare professionals can develop targeted dietary interventions for preventing and managing various health conditions. For instance, nutrigenomics can provide valuable insights into the dietary strategies that can be effective in managing obesity and diabetes. It can also inform interventions for cardiovascular diseases, where diet plays a crucial role in preventing and managing these conditions.
Furthermore, nutrigenomics can enhance athletic performance by tailoring nutritional strategies to an individual’s genetic predispositions. Understanding an athlete’s genetic variations can provide insights into their optimal macronutrient ratios, nutrient timing, and recovery strategies. By personalizing their nutrition plans based on their genetic profile, athletes can potentially optimize their athletic performance and enhance their overall well-being.
Challenges and Limitations of Nutrigenomics
While nutrigenomics holds immense promise, there are several challenges and limitations that need to be addressed. One of the main ethical considerations in personalized nutrition is the appropriate use of genetic information. Privacy and consent concerns arise when individuals undergo genetic testing to inform their personalized nutrition plans. It is crucial to ensure that individuals have full control over their genetic information and that it is used responsibly and ethically.
Another challenge is the accessibility and affordability of nutrigenomic services. Currently, genetic testing and personalized nutrition services can be costly and may not be readily available to all populations. Ensuring equitable access to these services is vital to prevent disparities in healthcare and to make personalized nutrition interventions accessible to diverse populations.
Additionally, the complexity of gene-diet interactions presents a challenge in implementing nutrigenomics effectively. Deciphering the intricate interplay between genes and dietary factors is a complex task that requires ongoing research and advancements in scientific methodologies. The current understanding of gene-diet interactions is still limited, and further research is needed to fully grasp the complexity of these interactions and their implications for personalized nutrition.
Technological Advancements in Nutrigenomics
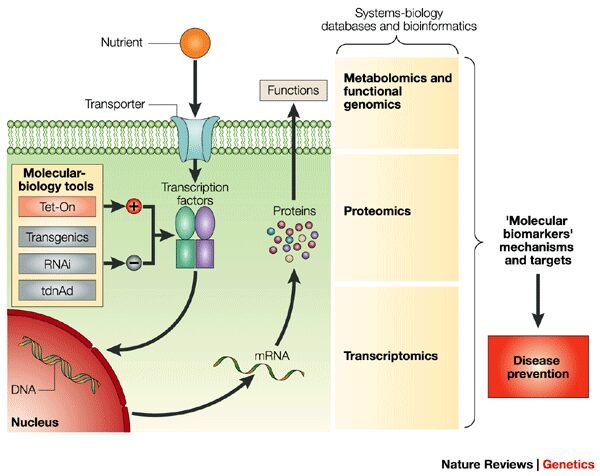
In recent years, there have been significant technological advancements that have the potential to propel the field of nutrigenomics forward. One such advancement is the emergence of advanced sequencing techniques. These techniques allow for the rapid and cost-effective analysis of an individual’s genetic makeup, providing researchers with valuable insights into their unique genomic variations. With these advanced sequencing techniques, scientists can further unravel the intricate relationship between genetics and nutrition.
Moreover, artificial intelligence (AI) has the potential to revolutionize nutrigenomics. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of genetic and nutritional data to identify patterns and make predictions about an individual’s dietary needs and responses. This integration of AI in nutrigenomics can enhance the accuracy and efficiency of personalized nutrition recommendations, further optimizing individual health outcomes.
However, it is essential to acknowledge the limitations of current technological applications in nutrigenomics. While advanced sequencing techniques and AI hold immense promise, they are still in the early stages of development. Further research and refinement of these technologies are needed to ensure their accuracy and reliability in personalized nutrition interventions.
This image is property of media.springernature.com.
Nutrigenomics and Healthcare Integration
Integrating nutrigenomics into mainstream healthcare practices holds great potential for revolutionizing preventive medicine. By incorporating genetic information into routine healthcare assessments, healthcare professionals can gain a comprehensive understanding of an individual’s genetic predispositions, allowing for targeted dietary interventions. This integration can enable early identification of individuals at higher risk for certain diseases, facilitating preventive measures through personalized nutrition plans.
Furthermore, nutrigenomics can be integrated into wellness programs to promote optimal health outcomes. By incorporating genetic information into wellness assessments, individuals can gain insights into their unique nutritional needs and make informed choices about their diets. This integration of nutrigenomics in wellness programs can empower individuals to take control of their health and make proactive choices to optimize their well-being.
However, the integration of nutrigenomics into healthcare practices presents several challenges. Healthcare professionals need to be adequately trained in the field of nutrigenomics to effectively utilize genetic information in their practice. Additionally, there is a need for standardized guidelines and protocols to ensure the proper use and interpretation of genetic information in the context of personalized nutrition. Overcoming these challenges will be crucial to realize the full potential of nutrigenomics in healthcare integration.
Public Education and Awareness about Nutrigenomics
Public understanding of nutrigenomics is vital for its successful implementation and acceptance. Educating the public about the significance of personalized nutrition and the role of genetic variations in dietary responses is essential. By increasing public awareness, individuals can make informed decisions about their dietary choices and understand the potential benefits of personalized nutrition interventions.
Bridging the knowledge gap between scientists and the general public is crucial. Communicating scientific findings in an accessible and understandable manner can empower individuals to actively engage in their health and nutrition. Creating educational resources, such as online tools, infographics, and educational programs, can help disseminate information about nutrigenomics to a broader audience.
Furthermore, integrating nutrigenomics into school curricula and community programs can foster a generation that is well-informed about the interplay between genetics and nutrition. Educating young individuals about the importance of personalized nutrition from an early age can have long-term positive effects on their health and well-being.
This image is property of foodnwellness.com.
Ethics in Nutrigenomics
In the context of nutrigenomics, ethical considerations are paramount. Privacy and consent concerns arise when individuals undergo genetic testing, as their genetic information becomes accessible to others. Struggling with the appropriate use and storage of genetic information is crucial to protect the privacy and autonomy of individuals.
Additionally, there is a concern about the possible misuse of genetic information in personalized nutrition. This information can be sensitive and can potentially be exploited for discriminatory purposes. Ensuring strict regulations and policies surrounding the use and accessibility of genetic information is essential to prevent any misuse and protect the well-being of individuals.
Furthermore, ensuring transparency and accountability in research and industry practices is vital. Researchers and practitioners in the field of nutrigenomics must adhere to strict ethical guidelines and ensure that their practices are based on solid scientific evidence. This transparency and accountability are necessary to build trust and ensure the responsible use of genetic information in personalized nutrition.
Nutrigenomics for Disease Management
Nutrigenomics has significant implications for disease management, particularly in conditions such as obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. Understanding an individual’s genetic variations can provide insights into their unique dietary needs and responses, allowing for targeted dietary interventions.
In managing obesity and diabetes, nutrigenomics can inform personalized nutrition strategies tailored to an individual’s genetic profile. By analyzing an individual’s genetic variations, healthcare professionals can identify dietary approaches that may be more effective for weight management and glycemic control. This personalized approach can improve the efficacy of interventions and promote better health outcomes.
Similarly, cardiovascular diseases can be managed more effectively through personalized nutrition plans informed by nutrigenomics. Understanding an individual’s genetic variations related to lipid metabolism, inflammation, and blood pressure regulation can help tailor dietary recommendations to reduce the risk of cardiovascular events and improve overall cardiovascular health.
However, it is important to note that further research is needed to fully understand the role of nutrigenomics in chronic diseases. While nutrigenomics offers promising insights, there are still many unanswered questions about the complex interplay between genes and dietary factors in disease management.

This image is property of ars.els-cdn.com.
Future Directions for Nutrigenomics
The field of nutrigenomics continues to evolve, offering exciting research areas and opportunities for further exploration. Emerging research areas include the study of the gut microbiome and its interaction with genes and diet. This burgeoning field, known as nutri-microbiomics, aims to unravel the complex relationship between the gut microbiome, genetic variations, and dietary responses. By understanding this interaction, scientists can potentially develop tailored dietary interventions to optimize gut health and overall well-being.
Anticipated developments in nutrigenomics include advancements in personalized nutrition technology. As sequencing techniques improve and become more affordable, genetic testing for personalized nutrition may become more accessible to the general population. This increased availability can further drive research and enhance the integration of personalized nutrition into healthcare and everyday life.
Despite the advancements and opportunities, several unresolved questions remain in the field of nutrigenomics. Researchers are still working to fully decode the complex gene-diet interactions, uncovering the specific mechanisms through which genes influence nutrient metabolism and dietary responses. Additionally, the long-term effects and efficacy of personalized nutrition interventions are still being explored. Future research endeavors aim to address these unanswered questions and refine our understanding of nutrigenomics.
Conclusion and Call to Action
Nutrigenomics is a cutting-edge field that has the potential to revolutionize the way we approach nutrition and health. By understanding the intricate interplay between genetics and nutrition, personalized nutrition strategies can be developed to optimize health outcomes. However, there is still much work to be done.
Further research is needed to enhance our understanding of the complexity of gene-diet interactions and the long-term effects of personalized nutrition interventions. This research requires collaboration between scientists, healthcare professionals, and policymakers to ensure that the latest advancements in nutrigenomics translate into meaningful and evidence-based interventions.
Additionally, public education and awareness about nutrigenomics are paramount. Empowering individuals to make informed decisions about their dietary choices and understand the potential benefits of personalized nutrition is essential. By bridging the knowledge gap and integrating nutrigenomics into educational curricula and community programs, we can create a society that embraces the power of personalized nutrition.
In conclusion, nutrigenomics has the potential to transform the field of nutrition and optimize individual health outcomes. With further research, technological advancements, and collaborative efforts, we can unlock the full potential of nutrigenomics and pave the way for a future where personalized nutrition is at the forefront of healthcare.
Related Posts: Interaction between genetic susceptibility to obesity and food intake on BMI in Finnish school-aged children, The Impact of Malnutrition on Epigenetics: Exploring the Relationship between Genetics and Nutrition, Understanding the Impact of Genetics on Health Through Nutrigenomics, How does epigenetics impact personalized nutrition strategies?, Benefits of Genome Sequencing in Nutrigenomics



